
Back تدخل حزب الله في الحرب الأهلية السورية Arabic مداخله حزبالله در جنگ داخلی سوریه Persian Intervention du Hezbollah dans la guerre civile syrienne French מעורבות חזבאללה במלחמת האזרחים בסוריה HE 헤즈볼라의 시리아 내전 관여 Korean
| Hezbollah involvement in the Syrian civil war | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Foreign Involvement in the Syrian civil war, Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict, and the Iran–Israel proxy conflict in the Syrian civil war | ||||||||
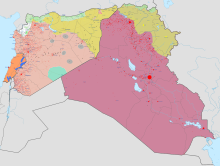 Military situation, as of April 9, 2019: (for a clickable version of the map without shaded areas, see here | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Belligerents | ||||||||
|
|
Supported by:
Supported by:
Supported by: |
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | ||||||||
|
1,139–1,250 fighters killed by March 2018[7] 1,736 fighters killed by March 2023 (per SOHR) [8] | ||||||||
Hezbollah involvement in the Syrian civil war has been substantial since the beginning of armed insurgency phase of the Syrian civil war in 2011, and evolved into active support for Syrian government forces and troop deployment from 2012 onwards. By 2014, Hezbollah was deployed across Syria.[9] Hezbollah has also been very active in preventing Al-Nusra Front and Islamic State penetration into Lebanon, being one of the most active forces in the Syrian civil war spillover in Lebanon.
In the past, Hezbollah has served a strategic arm of Iran in the region, playing a key role in the Iran–Israel and Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflicts. On a number of occasions, Hezbollah weapon convoys in Syria and Syrian-Lebanese border areas were attacked, presumably by the Israeli military. Hezbollah convoys and militant camps have also been attacked by various Syrian rebel factions.
Hezbollah's image in the Arab world - especially in Syria and Lebanon - has been greatly tarnished due to its sectarian activities throughout the course of the Syrian civil war.[10] Major religious leaders and activists, Sunni and Shia alike, have condemned Hezbollah, with many former supporters of Hezbollah becoming its fervent opponents for its stance in Syria. Shi'i cleric Subhi al-Tufayli, the group's founder and principal architect during 1980s, fiercely denounced Hezbollah for abandoning its founding principles and accused it of serving the hegemonic ambitions of Iran and Russia.[11][12][13]
- ^ "المهندس يكشف دور ايران وحزب الله بدعم العراق ويتحدث عن القتال بسوريا". Archived from the original on 2017-05-11. Retrieved 2020-05-09.
- ^ "New Experience of Hezbollah with Russian Military". 2 February 2016. Archived from the original on 28 July 2018. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
- ^ Rosenfeld, Jesse (11 January 2016). "Russia is Arming Hezbollah, Say Two of the Group's Field Commanders". The Daily Beast.
- ^ "Hezbollah says gets support, not orders, from Iran". Reuters. 7 February 2012. Archived from the original on 15 October 2015. Retrieved 2 July 2017.
- ^ "Iraq admits Lebanese Hezbollah and Iranian RG fight alongside Iraqi security forces - Iraqi News". Archived from the original on 15 June 2018. Retrieved 28 July 2018.
- ^ "Syrian rebels pour men and missiles into frontlines". The Fiscal Times. Retrieved 17 October 2015.
- ^ "Estimate of Hezbollah's fatalities during the Syrian civil war". 11 March 2019. Retrieved 18 August 2022.
- ^ "Syrian Revolution 12 years on | Nearly 614,000 persons killed since the onset of the revolution in March 2011". SOHR. 15 March 2023. Archived from the original on 15 March 2023. Retrieved 15 March 2023.
- ^ "Hezbollah in Syria's war". Archived from the original on 2018-06-12. Retrieved 2015-02-19.
- ^ Porter, Lizzie (5 October 2020). "How the Arab world turned against Hezbollah". Prospect Magazine. Archived from the original on 17 May 2023.
- ^ Mansour, David Clark, Renad, Michael (20 November 2014). "Rethinking Sadr: From Firebrand to Iraqi Statesman?". Carnegie Middle East Center. Archived from the original on 28 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ El-Bar, Karim (30 December 2016). "'They exploited sectarianism': Former Hezbollah leader Tufayli talks Iran, Syria". Middle East Eye. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021.
- ^ McGregor, Andrew (14 June 2013). "Muslim Brother's Spiritual Leader Yusuf al Qaradawi condemns Hezbollah" (PDF). XI (12). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 March 2023 – via The Jamestown Foundation.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)