
Back تاريخ نظرية الحقل الكمومي Arabic কোয়ান্টাম ক্ষেত্র তত্ত্বের ইতিহাস Bengali/Bangla Història de la teoria quàntica de camps Catalan Historia de la teoría cuántica de campos Spanish Histoire de la théorie quantique des champs French 場の量子論の歴史 Japanese 양자장론의 역사 Korean ਕੁਆਂਟਮ ਫੀਲਡ ਥਿਊਰੀ ਦਾ ਇਤਿਹਾਸ Punjabi د کوانټوم میدان د تیورۍ تاریخچه Pashto/Pushto História da teoria quântica de campos Portuguese
| Quantum field theory |
|---|
 |
| History |
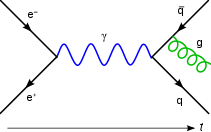
In particle physics, the history of quantum field theory starts with its creation by Paul Dirac, when he attempted to quantize the electromagnetic field in the late 1920s. Major advances in the theory were made in the 1940s and 1950s, leading to the introduction of renormalized quantum electrodynamics (QED). The field theory behind QED was so accurate and successful in predictions that efforts were made to apply the same basic concepts for the other forces of nature. Beginning in 1954, the parallel was found by way of gauge theory, leading by the late 1970s, to quantum field models of strong nuclear force and weak nuclear force, united in the modern Standard Model of particle physics.
Efforts to describe gravity using the same techniques have, to date, failed. The study of quantum field theory is still flourishing, as are applications of its methods to many physical problems. It remains one of the most vital areas of theoretical physics today, providing a common language to several different branches of physics.