
Back تاريخ الإمبراطورية البيزنطية Arabic Гісторыя Візантыі Byelorussian Història de l'Imperi Romà d'Orient Catalan Geschichte des Byzantinischen Reiches German Ιστορία της Βυζαντινής Αυτοκρατορίας Greek Historia del Imperio bizantino Spanish Bütsantsi ajalugu Estonian Histoire de l'Empire byzantin French Storia dell'impero bizantino Italian Историја на Византија Macedonian
| History of the Byzantine Empire |
|---|
 |
| Preceding |
| Early period (330–717) |
| Middle period (717–1204) |
| Late period (1204–1453) |
| Timeline |
| By topic |
|
|
The Byzantine Empire's history is generally periodised from late antiquity until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453 AD. From the 3rd to 6th centuries, the Greek East and Latin West of the Roman Empire gradually diverged, marked by Diocletian's (r. 284–305) formal partition of its administration in 285,[1] the establishment of an eastern capital in Constantinople by Constantine I in 330,[n 1] and the adoption of Christianity as the state religion under Theodosius I (r. 379–395), with others such as Roman polytheism being proscribed. Under the reign of Heraclius (r. 610–641), the Empire's military and administration were restructured and adopted Greek for official use instead of Latin.[3] While there was an unbroken continuity in administration and other features of Roman society, historians have often distinguished the Byzantine epoch from earlier eras in Roman history for reasons including the imperial seat moving from Rome to Constantinople and the predominance of Greek instead of Latin.[4]
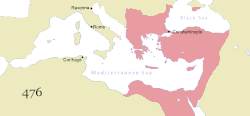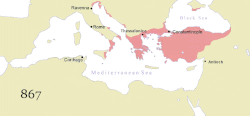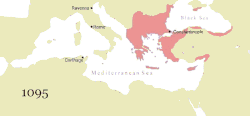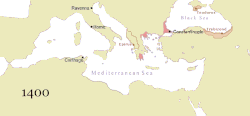
The borders of the Empire evolved significantly over its existence, as it went through several cycles of decline and recovery. During the reign of Justinian I (r. 527–565), the Empire reached its greatest extent after reconquering much of the historically Roman western Mediterranean coast, including north Africa, Italy, and Rome itself, which it held for two more centuries. During the reign of Maurice (r. 582–602), the Empire's eastern frontier was expanded and the north stabilised. However, his assassination caused a two-decade-long war with Sassanid Persia which exhausted the Empire's resources and contributed to major territorial losses during the Muslim conquests of the 7th century. In a matter of years the Empire lost its richest provinces, Egypt and Syria, to the Arabs.[5]
During the Macedonian dynasty (9th–11th centuries), the Empire again expanded and experienced a two-century long renaissance, which came to an end with the loss of much of Asia Minor to the Seljuk Turks after the Battle of Manzikert in 1071. This battle opened the way for the Turks to settle in Anatolia as a homeland. The final centuries of the Empire exhibited a general trend of decline. It struggled to recover during the 12th century, but was delivered a mortal blow during the Fourth Crusade, when Constantinople was sacked and the Empire dissolved and divided into competing Byzantine Greek and Latin realms. Despite the eventual recovery of Constantinople and re-establishment of the Empire in 1261, Byzantium remained only one of several small rival states in the area for the final two centuries of its existence. Its remaining territories were progressively annexed by the Ottomans over the 15th century. The Fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 finally ended the Roman Empire.
- ^ Treadgold 1997, p. 847.
- ^ Benz 1963, p. 176.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 1969, pp. 105–107, 109; Norwich 1998, p. 97; Haywood 2001, pp. 2.17, 3.06, 3.15.
- ^ Millar 2006, pp. 2, 15; James 2010, p. 5; Freeman 1999, pp. 431, 435–37, 459–62; Baynes & Moss 1948, p. xx; Ostrogorsky 1969, p. 27; Kaldellis 2007, pp. 2–3; Kazhdan & Constable 1982, p. 12; Norwich 1998, p. 383.
- ^ John Haldon, Warfare, State And Society In The Byzantine World 560–1204, p.47
Cite error: There are <ref group=n> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=n}} template (see the help page).