
Back نسبة الجنس البشري Arabic Séks rasio manusa BAN लिंगानुपात Bihari মানব লিঙ্গানুপাত Bengali/Bangla نسبت جنسی انسانی Persian Sexe-ratio chez l'être humain French लिंगानुपात Hindi Rasio jenis kelamin manusia ID Човеков полов сооднос Macedonian സ്ത്രീപുരുഷാനുപാതം Malayalam
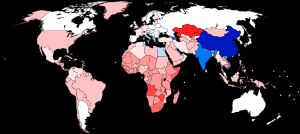


The human sex ratio is the ratio of males to females in a population in the context of anthropology and demography. In humans, the natural sex ratio at birth is slightly biased towards the male sex. It is estimated to be about 1.05[1] or 1.06[2] or within a narrow range from 1.03 to 1.06[3] males per female. The sex ratio for the entire world population is approximately 101 males to 100 females (2020 est.).[4]
The sex ratios at birth and of the total population are affected by various factors including natural factors, exposure to pesticides and environmental contaminants,[5][6] war casualties, effects of war on men, sex-selective abortions, infanticides,[7] aging, gendercide, problems with birth registration and sex differences in life expectancy.[1]
Human sex ratios, either at birth or in the population as a whole, can be reported in any of four ways: the ratio of males to females, the ratio of females to males, the proportion of males, or the proportion of females. If there are 108,000 males and 100,000 females the ratio of males to females is 1.08 and the proportion of males is 51.9%. Scientific literature often uses the proportion of males. This article uses the ratio of males to females, unless specified otherwise.
- ^ a b "World Health Organization, Sex Ratio". SEARO.[dead link]
- ^ Grech, Victor; Savona-Ventura, Charles; Vassallo-Agius, P (27 April 2002). "Unexplained differences in sex ratios at birth in Europe and North America". BMJ: British Medical Journal. 324 (7344): 1010–1011. doi:10.1136/bmj.324.7344.1010. PMC 102777. PMID 11976243.
- ^ Chao, Fengqing; Gerland, Patrick; Cook, Alex R.; Alkema, Leontine (7 May 2019). "Systematic assessment of the sex ratio at birth for all countries and estimation of national imbalances and regional reference levels". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 116 (19): 9303–9311. Bibcode:2019PNAS..116.9303C. doi:10.1073/pnas.1812593116. PMC 6511063. PMID 30988199.
- ^ "CIA Fact Book". The Central Intelligence Agency of the United States. 29 November 2021.
- ^ "How pollution may be changing the ratio of girls to boys". Stir.ac.uk. 18 June 2014. Retrieved 6 January 2018.
- ^ Davis, D. L.; Gottlieb, M. B.; Stampnitzky, J. R. (1998). "Reduced ratio of male to female births in several industrial countries: A sentinel health indicator?" (PDF). JAMA. 279 (13): 1018–23. doi:10.1001/jama.279.13.1018. PMID 9533502.
- ^ Very high sex ratios were common in even late medieval Europe, which may indicate sex-selective infanticide. Josiah Cox Russell, 1958, Late Ancient and Medieval Population, pp. 13–17.