Back Waterstofselenied Afrikaans سيلينيد الهيدروجين Arabic سلنید هیدروژن AZB Селенавадарод Byelorussian Selan Czech Selenwasserstoff German Υδροσελήνιο Greek Seleniuro de hidrógeno Spanish سلنید هیدروژن Persian Seleenivety Finnish
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hydrogen selenide
| |||
| Other names
Hydroselenic acid
selane selenium hydride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.071 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2202 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| H2Se | |||
| Molar mass | 80.98 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Odor | decayed horseradish[1] | ||
| Density | 3.553 g/dm3 | ||
| Melting point | −65.73 °C (−86.31 °F; 207.42 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −41.25 °C (−42.25 °F; 231.90 K) | ||
| 0.70 g/100 mL | |||
| Solubility | soluble in CS2, phosgene | ||
| Vapor pressure | 9.5 atm (21°C)[1] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.89 | ||
| Conjugate acid | Selenonium | ||
| Conjugate base | Selenide | ||
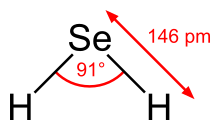
| Structure | |||
| Bent | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Extremely toxic and flammable | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H220, H330, H410 | |||
| P210, P260, P271, P273, P284, P304+P340, P310, P320, P377, P381, P391, P403, P403+P233, P405, P410+P403, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | flammable gas | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
0.3 ppm (guinea pig, 8 hr) 5.9 ppm (rat, 1 hr)[2] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.05 ppm (0.2 mg/m3)[1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.05 ppm (0.2 mg/m3)[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1 ppm[1] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0284 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
H2O H2S H2Te H2Po | ||
Other cations
|
Na2Se Ag2Se | ||
Related compounds
|
Arsine | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Hydrogen selenide is an inorganic compound with the formula H2Se. This hydrogen chalcogenide is the simplest and most commonly encountered hydride of selenium. H2Se is a colorless, flammable gas under standard conditions. It is the most toxic selenium compound[3] with an exposure limit of 0.05 ppm over an 8-hour period.[4][5] Even at extremely low concentrations, this compound has a very irritating smell resembling that of decayed horseradish or "leaking gas", but smells of rotten eggs at higher concentrations.
- ^ a b c d e NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0336". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Hydrogen selenide". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ http://www.epa.gov/ttnatw01/hlthef/selenium.html, US Environmental Protection Agency, Air Toxins website
- ^ "CDC - Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH): Hydrogen selenide (as Se) - NIOSH Publications and Products". www.cdc.gov. 2018-11-02. Retrieved 2023-01-09.
- ^ https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/81-123/pdfs/0336.pdf Occupational Health Guideline for Hydrogen Selenide, The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, 1978