
Back ك. ر. نارايانان Arabic ك. ر. نارايانان ARZ কে আৰ নাৰায়ণন Assamese Kocheril Raman Narayanan AST कोच्चेरील रामन नारायणन AWA Качэрыл Раман Нараянан Byelorussian কে. আর. নারায়ণন Bengali/Bangla Kocheril Raman Narayanan Breton Kocheril Raman Narayanan Catalan Kóččeril Ráman Nárájanan Czech
K. R. Narayanan | |
|---|---|
 Official portrait, 2000 | |
| 10th President of India | |
| In office 25 July 1997 – 25 July 2002 | |
| Prime Minister | |
| Vice President | Krishan Kant |
| Preceded by | Shankar Dayal Sharma |
| Succeeded by | A. P. J. Abdul Kalam |
| 9th Vice President of India | |
| In office 27 October 1992 – 24 July 1997 | |
| President | Shankar Dayal Sharma |
| Prime Minister | |
| Preceded by | Shankar Dayal Sharma |
| Succeeded by | Krishan Kant |
| Member of Parliament, Lok Sabha | |
| In office 1984–1992 | |
| Preceded by | A. K. Balan |
| Constituency | Ottapalam |
| Indian Ambassador to United States | |
| In office 1980–1984 | |
| Preceded by | Nanabhoy Palkhivala |
| Indian Ambassador to China | |
| In office 7 July 1976 – 11 November 1978 | |
| Succeeded by | Ram Sathe |
| Personal details | |
| Born | 27 October 1920 Uzhavoor, Kingdom of Travancore, British India (now Kerala, India) |
| Died | 9 November 2005 (aged 85) New Delhi, Delhi, India |
| Spouse | |
| Children | 2 (including Chitra Narayanan) |
| Alma mater | |
| Signature | 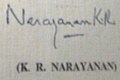 |
Kocheril Raman "K. R." Narayanan ([kot͡ʃeɾɪl ɾəməɳ nɑɾɑjəɳən]) 27 October 1920 – 9 November 2005)[1][2] was an Indian statesman, diplomat, academic, and politician who served as the ninth vice president of India from 1992 to 1997 and tenth president of India from 1997 to 2002.
Narayanan was born in Perumthanam, Uzhavoor village, in the princely state of Travancore (present day Kottayam district, Kerala) into a Hindu family. After a brief stint with journalism and then studies at the London School of Economics with the assistance of a scholarship, Narayanan began his career in India as a member of the Indian Foreign Service in the Nehru administration. He served as ambassador to a number of countries, most principally to the United States and China, and was referred by Nehru as "the best diplomat of the country".[3] He entered politics at Indira Gandhi's request and won three successive general elections to the Lok Sabha and served as a Minister of State in Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi's cabinet. Elected as vice president in 1992, Narayanan went on to become president in 1997 and became the first Dalit to occupy either position.
Narayanan is regarded as an independent and assertive president who set several precedents and enlarged the scope of India's highest constitutional office. He described himself as a "working president" who worked "within the four corners of the Constitution"; something midway between an "executive president" who has direct power and a "rubber-stamp president" who endorses government decisions without question or deliberation.[4] He used his discretionary powers as a president and deviated from convention and precedent in many situations, including – but not limited to – the appointment of the Prime Minister in a hung Parliament, in dismissing a state government and imposing President's rule there at the suggestion of the Union Cabinet, and during the Kargil conflict. He presided over the golden jubilee celebrations of Indian independence and in the country's general election of 1998, he became the first Indian president to vote when in office, setting another new precedent. As of 2023, he remains the last Indian to have been elected president, while serving as Vice President.
- ^ Burns, John F. (26 July 1997). "Lowest-Caste Hindu Takes Office as India's President". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 9 September 2020.
- ^ "Kocheril Raman Narayanan | president of India". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 9 September 2020.
- ^ Manmohan Singh: Condolence message Archived 27 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 24 February 2006.
- ^ "Shri K. R. Narayanan, President of India, in Conversation with N. Ram on Doordarshan and All India Radio" (PDF). The Hindu. 14 August 1998. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 November 2005. Retrieved 25 October 2015.