
Back سلفات الكيراتان Arabic Sulfat de queratan Catalan Queratán sulfato Spanish کراتان سولفات Persian Kerataanisulfaatti Finnish Sulfate de kératane French Queratán sulfato Galician Keratan-sulfat Croatian Cheratan solfato Italian ケラタン硫酸 Japanese
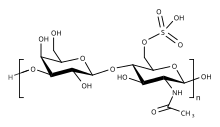
Keratan sulfate (KS), also called keratosulfate, is any of several sulfated glycosaminoglycans (structural carbohydrates) that have been found especially in the cornea, cartilage, and bone. It is also synthesized in the central nervous system where it participates both in development[1] and in the glial scar formation following an injury.[2] Keratan sulfates are large, highly hydrated molecules which in joints can act as a cushion to absorb mechanical shock.
- ^ Miller B, Sheppard AM, Pearlman AL (April 1997). "Developmental expression of keratan sulfate-like immunoreactivity distinguishes thalamic nuclei and cortical domains". J. Comp. Neurol. 380 (4): 533–52. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19970421)380:4<533::AID-CNE9>3.0.CO;2-2. PMID 9087531.
- ^ Zhang H, Uchimura K, Kadomatsu K (November 2006). "Brain keratan sulfate and glial scar formation". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1086 (1): 81–90. Bibcode:2006NYASA1086...81Z. doi:10.1196/annals.1377.014. PMID 17185507.