Back Kereta Api Indonesia German Kereta Api Indonesia Esperanto کرتا آپی Persian Kereta Api Indonesia Finnish Compagnie des chemins de fer indonésiens French Kereta Api Indonesia ID Kereta Api Indonesia Italian クレタ・アピ・インドネシア Japanese PT. Kereta Api Indonesia JV PT Kereta Api Indonesia Malay
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2022) |
This article may require copy editing for grammar, style, cohesion, tone, or spelling. (March 2024) |
 Logo used since 28 September 2020 | |
 CC 201(GE U18C) is a Locomotive owned by Kereta Api Indonesia | |
| Formerly | Indonesian State Railways (DKARI/DKA/PNKA/PJKA) (1945–1990) Indonesian Railway Public Corporation (Perumka) (1990–1995) |
|---|---|
| Company type | State-owned perseroan terbatas |
| IDX: KAII (bonds) | |
| Headquarters | , Indonesia |
Key people | Said Aqil Siradj (chairman of the advisory board) Didiek Hartantyo (CEO) |
| Revenue | |
| Total assets | |
| Owner | Government of Indonesia |
Number of employees | 27,396 (2017)[1] |
| Subsidiaries | KAI Commuter KAI Bandara KAI Logistik KAI Wisata KAI Properti KAI Services |
| Website | www |
 | |
 | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Fleet | List
|
| Headquarters | Bandung, Indonesia |
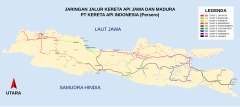
| Locale | Java, Sumatra (Aceh, North Sumatra, West Sumatra, South Sumatra, and Lampung), Sulawesi (South Sulawesi) |
| Dates of operation | 1945–present |
| Predecessor | See: List of railway companies in the Dutch East Indies |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) (Most of railway lines) 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) (Aceh, Sulawesi, LRT Jabodebek) |
| Previous gauge | 750 mm (2 ft 5+1⁄2 in) (Aceh tramway gauge)[3] 600 mm (1 ft 11+5⁄8 in) (tramway gauge)[3] |
| Electrification | 1500 V DC overhead wiring for KCI operation 750 V DC third rail for Palembang LRT, and Jabodebek LRT operation[4] |
| Length | 5,042 kilometres (3,133 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,246 m (4,088 ft) (Cikajang railway station)[5] |
PT Kereta Api Indonesia (Persero) (lit. 'Indonesian Railways (State-owned) Limited', abbreviated as PT KAI or simply KAI) is a major railway operator in Indonesia and one of the public railway companies in the country. It is state-owned and pays track access charges. Its headquarters are located in Bandung, West Java. In 2019, KAI carried 429 million passengers and 47.2 million tonnes of cargo.[6]
- ^ a b c d "Annual Report" (PDF). Indonesia Railway Company. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 February 2022. Retrieved 31 July 2018.
- ^ "Hanya Tingkatkan Pelayanan, Bisnis PT KAI Tumbuh 24 Persen". Archived from the original on 17 September 2017. Retrieved 4 October 2022.
- ^ a b Nasir, Muhammad; Azril, Andi (28 June 2003). "Pembangunan Rel KA Langkat-Banda Aceh Terbengkalai". Liputan6.com (in Indonesian). Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ Putra, Aji YK (12 April 2018). "Ini Perbedaan LRT di Palembang dan Jakarta". KOMPAS (in Indonesian). Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ^ "Mempercantik Kembali Sinyal Stasiun Cikajang-Garut" (in Indonesian). 11 May 2017. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ "KAI: 2019, Jumlah Penumpang Kereta Naik 4 Juta". Tempo (in Indonesian). 10 February 2020. Retrieved 17 December 2021.[permanent dead link]