
Back Lambda-KDM-model Afrikaans نموذج لامبدا-سي دي إم Arabic Lambda-CDM model Azerbaijani Модел Ламбда-CDM Bulgarian ল্যামডা-সিডিএম নকশা Bengali/Bangla Model Lambda-CDM Catalan Model ΛCDM Czech Lambda-CDM-Modell German Μοντέλο Lambda-CDM Greek Modelo Lambda-CDM Spanish
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2024) |
| Part of a series on |
| Physical cosmology |
|---|
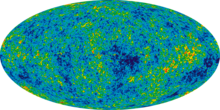 |
The Lambda-CDM, Lambda cold dark matter, or ΛCDM model is a mathematical model of the Big Bang theory with three major components:
- a cosmological constant, denoted by lambda (Λ), associated with dark energy;
- the postulated cold dark matter, denoted by CDM;
- ordinary matter.
It is the current standard model of Big Bang cosmology,[1] as it is the simplest model that provides a reasonably good account of:
- the existence and structure of the cosmic microwave background;
- the large-scale structure in the distribution of galaxies;
- the observed abundances of hydrogen (including deuterium), helium, and lithium;
- the accelerating expansion of the universe observed in the light from distant galaxies and supernovae.
The model assumes that general relativity is the correct theory of gravity on cosmological scales. It emerged in the late 1990s as a concordance cosmology, after a period of time when disparate observed properties of the universe appeared mutually inconsistent, and there was no consensus on the makeup of the energy density of the universe.
The ΛCDM model has been successful in modeling broad collection of astronomical observations over decades. Remaining issues have lead to many alternative models and challenges the assumptions of the ΛCDM model.[2]
- ^ Deruelle, Nathalie; Uzan, Jean-Philippe (2018-08-30). de Forcrand-Millard, Patricia (ed.). Relativity in Modern Physics (1 ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198786399.001.0001. ISBN 978-0-19-878639-9.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Snowmass21was invoked but never defined (see the help page).