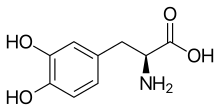
Levodopa, also known as L-DOPA and sold under many brand names, is a dopaminergic medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and certain other conditions like dopamine-responsive dystonia and restless legs syndrome.[3] The drug is usually used and formulated in combination with a peripherally selective aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AAAD) inhibitor like carbidopa or benserazide.[3] Levodopa is taken by mouth, by inhalation, through an intestinal tube, or by administration into fat (as foslevodopa).[3]
Side effects of levodopa include nausea, the wearing-off phenomenon, dopamine dysregulation syndrome, and levodopa-induced dyskinesia, among others.[3] The drug is a centrally permeable monoamine precursor and prodrug of dopamine and hence acts as a dopamine receptor agonist.[3] Chemically, levodopa is an amino acid, a phenethylamine, and a catecholamine.[3]
Levodopa was first synthesized and isolated in the early 1910s.[3] The antiparkinsonian effects of levodopa were discovered in the 1950s and 1960s.[3] Following this, it was introduced for the treatment of Parkinson's disease in 1970.[3]
- ^ Howard ST, Hursthouse MB, Lehmann CW, Poyner EA (1995). "Experimental and theoretical determination of electronic properties in Ldopa". Acta Crystallogr. B. 51 (3): 328–337. Bibcode:1995AcCrB..51..328H. doi:10.1107/S0108768194011407. S2CID 96802274.
- ^ a b "Levodopa Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 12 July 2019. Retrieved 27 September 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Whitfield AC, Moore BT, Daniels RN (December 2014). "Classics in chemical neuroscience: levodopa". ACS Chem Neurosci. 5 (12): 1192–1197. doi:10.1021/cn5001759. PMID 25270271.