
Back Tibettaans Afrikaans اللغة التبتية Arabic لغه تيبيتى ARZ Idioma tibetanu AST तिब्बती भाषा AWA Tibet dili Azerbaijani Basa Tibét BAN Тыбецкая мова Byelorussian Тыбэцкая мова BE-X-OLD Тибетски език Bulgarian
| Lhasa Tibetan | |
|---|---|
| བོད་སྐད་ | |
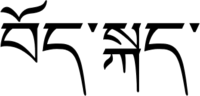 | |
| Native to | Lhasa |
| Region | Tibet Autonomous Region, Ü-Tsang |
Native speakers | (1.2 million cited 1990 census)[1] |
Sino-Tibetan
| |
Early forms | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Regulated by | Committee for the Standardisation of the Tibetan Language[note 1] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | bo |
| ISO 639-2 | tib (B) bod (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | bod |
| Glottolog | tibe1272 |
| Linguasphere | 70-AAA-ac |
Lhasa Tibetan[a] (Tibetan: ལྷ་སའི་སྐད་, Wylie: Lha-sa'i skad, THL: Lhaséké, ZYPY: Lasägä) or Standard Tibetan (Tibetan: བོད་སྐད་, Wylie: Bod skad, THL: Böké, ZYPY: Pögä, IPA: [pʰø̀k˭ɛʔ], or Tibetan: བོད་ཡིག་, Wylie: Bod yig, THL: Böyik, ZYPY: Pöyig)[citation needed] is the Tibetan dialect spoken by educated people of Lhasa, the capital of the Tibetan Autonomous Region.[2] It is an official language of the Tibet Autonomous Region.[3]
In the traditional "three-branched" classification of the Tibetic languages, the Lhasa dialect belongs to the Central Tibetan branch (the other two being Khams Tibetan and Amdo Tibetan).[4] In terms of mutual intelligibility, speakers of Khams Tibetan are able to communicate at a basic level with Lhasa Tibetan, while Amdo speakers cannot.[4] Both Lhasa Tibetan and Khams Tibetan evolved to become tonal and do not preserve the word-initial consonant clusters, which makes them very far from Classical Tibetan, especially when compared to the more conservative Amdo Tibetan.[5][6]
- ^ Lhasa Tibetan at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ DeLancey, Scott (2017). "Chapter 19: Lhasa Tibetan". In Graham Thurgood and Randy J. LaPolla (ed.). The Sino-Tibetan Languages, 2nd edition. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-367-57045-3.
- ^ "Fifty Years of Democratic Reform in Tibet". Official Chinese government site. 2009-03-02. Archived from the original on 2015-12-08. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ a b Gelek, Konchok (2017). "Variation, contact, and change in language: Varieties in Yul shul (northern Khams)". International Journal of the Sociology of Language (245): 91-92.
- ^ Makley, Charlene; Dede, Keith; Hua, Kan; Wang, Qingshan (1999). "The Amdo Dialect of Labrang" (PDF). Linguistics of the Tibeto-Burman Area. 22 (1): 101. doi:10.32655/LTBA.22.1.05. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-05.
- ^ Reynolds, Jermay J. (2012). Language variation and change in an Amdo Tibetan village: Gender, education and resistance (PDF) (PhD thesis). Graduate School of Arts and Sciences of Georgetown University. p. 19-21. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-08-12.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).