
Back لندان Arabic قامابنزن هقزاکلراید AZB Lindà Catalan Lindan Czech Lindan Welsh Lindan German Λινδάνιο Greek Lindano Spanish Lindano Basque گامابنزن هگزاکلراید Persian
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682651 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 91% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic cytochrome P-450 oxygenase system |
| Elimination half-life | 18 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.365 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
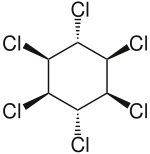
| Formula | C6H6Cl6 |
| Molar mass | 290.81 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Lindane, also known as gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane (γ-HCH), gammaxene, Gammallin and benzene hexachloride (BHC),[3] is an organochlorine chemical and an isomer of hexachlorocyclohexane that has been used both as an agricultural insecticide and as a pharmaceutical treatment for lice and scabies.[4][5]
Lindane is a neurotoxin that interferes with GABA neurotransmitter function by interacting with the GABAA receptor-chloride channel complex at the picrotoxin binding site. In humans, lindane affects the nervous system, liver, and kidneys, and may well be a carcinogen.[6][7] Whether lindane is an endocrine disruptor is unclear.[8][9][10]
The World Health Organization classifies lindane as "moderately hazardous", and its international trade is restricted and regulated under the Rotterdam Convention on Prior Informed Consent.[11] In 2009, the production and agricultural use of lindane was banned under the Stockholm Convention on persistent organic pollutants.[2][12] A specific exemption to that ban allows it to continue to be used as a second-line pharmaceutical treatment for lice and scabies.[13]
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ a b c "Listing of POPs in the Stockholm Convention". Stockholm Convention.
- ^ Brandenberger H, Maes RA (1997). Analytical toxicology: for clinical, forensic, and pharmaceutical chemists. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. p. 243. ISBN 978-3-11-010731-9. Retrieved 2009-05-10.
- ^ "Professional Drug Information: Lindane". Archived from the original on 2018-08-20. Retrieved 2020-02-28.
- ^ "The North American Regional Action Plan (NARAP) on Lindane and Other Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) Isomers" (PDF). Commission for Environmental Cooperation. 2013. Retrieved 2020-02-28.
- ^ "Toxicologic profile for alpha-, beta, gamma- and delta-hexachlorocyclohenxane" (PDF). Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. August 2005.
- ^ "Lindane Voluntary Cancellation and RED Addendum Fact Sheet". US EPA. July 2006. Archived from the original on 2006-10-06.
- ^ "Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Potential of Lindane, PC. Code: 009001" (PDF). U.S. EPA. 2001. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-09-28.
- ^ "Summaries & Evaluations: HEXACHLOROCYCLOHEXANES (Group 2B)". International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). 1998-03-02.
- ^ World Health Organization (WHO) (2004). "Lindane in Drinking Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality" (PDF). Retrieved 2020-02-28.
- ^ World Health Organization, The WHO Recommended Classification of Pesticides by Hazard, 2005.
- ^ Press Release - COP4 - Geneva, 8 May 2009: Governments unite to step-up reduction on global DDT reliance and add nine new chemicals under international treaty
- ^ Eliane Engeler, "UN: Treaty expanded by 9 more dangerous chemicals", Associated Press 2009-05-09