
Back Marlins Park Catalan LoanDepot Park German LoanDepot Park Spanish Marlins Park Basque LoanDepot Park French Marlins Park Galician मार्लिंस पार्क Hindi LoanDepot Park Italian ローンデポ・パーク Japanese 론디포 파크 Korean
This article contains too many or overly lengthy quotations. (November 2019) |
 | |
 LoanDepot Park in November 2024 | |
| Former names | Marlins Park (2012–2020) |
|---|---|
| Address | 501 Marlins Way |
| Location | Miami, Florida, United States |
| Coordinates | 25°46′41″N 80°13′11″W / 25.77806°N 80.21972°W |
| Public transit | |
| Parking | Four main parking garages and six surface lots |
| Owner | Miami-Dade County |
| Operator | Miami Marlins LP |
| Capacity | 36,742 37,442 (with standing room)[2] 34,000 (football)[3] |
| Record attendance | 37,446 (March 11, 2017 World Baseball Classic. USA vs Dom. Rep.)[4] |
| Field size | Left field line – 344 ft (105 m) Left-center power alley – 386 ft (118 m) Center field – 400 ft (120 m) Right-center power alley – 387 ft (118 m) Right field line – 335 ft (102 m) Backstop: – 47 ft (14.3 m) 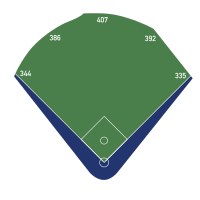 |
| Acreage | 928,000 sq ft (86,200 m2) |
| Surface |
|
| Construction | |
| Broke ground | July 1, 2009 (Start of construction preparations) July 18, 2009 (Ceremonial groundbreaking)[6] |
| Opened | March 5, 2012 (High school baseball game) March 6, 2012 (exhibition game) April 1, 2012 (spring training game) April 4, 2012 (regular season) |
| Construction cost | US$634 million[7] ($841 million in 2023 dollars[8]) |
| Architect | Populous[9] |
| Project manager | International Facilities Group[10] |
| Structural engineer | Bliss & Nyitray, Inc (bowl and track) Walter P Moore (roof) |
| Services engineer | M-E Engineers, Inc.[11] |
| General contractor | Hunt/Moss Joint Venture |
| Main contractors | MARS Contractors Inc.[12] John J. Kirlin, LLC.[13] Structal – Heavy Steel Construction, A division of Canam Group (roof)[14] |
| Tenants | |
| Miami Marlins (MLB) (2012–present) Miami Beach Bowl (NCAA) (2014–2016) | |
LoanDepot Park (officially stylized as loanDepot park, and named Marlins Park until 2021) is a retractable roof stadium located in Miami, Florida, United States. It is the ballpark of Major League Baseball's Miami Marlins.[15] It is located on 17 acres (6.9 ha) on the site of the former Miami Orange Bowl in Little Havana about 2 miles (3 km) west of Downtown Miami. Construction was completed in March 2012 for the 2012 season.
LoanDepot Park was LEED certified as the greenest MLB park in 2012.[16] The building is the sixth MLB stadium to have a retractable roof. With a seating capacity of 37,442,[2] it is the third-smallest stadium in Major League Baseball by official capacity, and the smallest by actual capacity. The facility hosted a second-round pool of the 2013 World Baseball Classic, a first-round pool of the 2017 World Baseball Classic, the 2017 Major League Baseball All-Star Game, and the championship game of the 2023 World Baseball Classic. The park also hosts soccer matches, fundraising galas, and other events during the winter. It also hosted the Miami Beach Bowl from 2014 through 2016.
The stadium is designed in a neomodern form of baseball architecture.
- ^ "Service to Marlins Park". Miami-Dade County. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ a b Herrera, Margaux (April 1, 2012). "Marlins Add 3,001 Parking Spaces". The Miami Herald. Retrieved April 3, 2012.
- ^ "Marlins Park Facts & Figures". Baseball Pilgrimages. Retrieved December 24, 2015.
- ^ "World Baseball Classic".
- ^ Spedden, Zach (December 4, 2019). "2020 Marlins Park Changes: Shorter Dimensions, Synthetic Turf". Ballpark Digest. Retrieved December 5, 2019.
- ^ Frisaro, Joe (June 8, 2009). "Marlins to Break Ground for New Ballpark". MLB Advanced Media, L.P. Retrieved June 8, 2009.[dead link]
- ^ Rabin, Charles (May 28, 2012). "Miami-Dade Challenging $1.7 Million of Marlins Expenses at New Ballpark". The Miami Herald. Retrieved May 28, 2012.
- ^ 1634–1699: McCusker, J. J. (1997). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States: Addenda et Corrigenda (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1700–1799: McCusker, J. J. (1992). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1800–present: Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis. "Consumer Price Index (estimate) 1800–". Retrieved February 29, 2024.
- ^ "Marlins Park". Populous.
- ^ "IFG – Florida Marlins Ballpark". International Facilities Group. January 28, 2009. Retrieved May 4, 2012.
- ^ "M-E Engineers, Inc". M-E Engineers, Inc. Retrieved May 4, 2012.
- ^ "Welcome to MARS Contractors, Inc". Mars Contractors. Archived from the original on April 25, 2012. Retrieved May 4, 2012.
- ^ "Kirlin mechanical contractors – About Us :: Company Overview". John J Kirlin, LLC. Retrieved May 4, 2012.
- ^ "Projects: Marlins Park". Canam Steel Corporation. Retrieved March 8, 2013.
- ^ Tompkins, Wayne (May 24, 2007). "Commissioners OK Plan to Have Marlins Change Name, Spring-Training Site". Miami Today. Retrieved May 4, 2012.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
leed goldwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).


