
Back حمض المالونيك Arabic Malon turşusu Azerbaijani مالونیک اسید AZB Малонова киселина Bulgarian Àcid malònic Catalan Kyselina malonová Czech Malonsäure German Malonata acido Esperanto Ácido malónico Spanish Azido maloniko Basque
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propanedioic acid[1] | |
| Other names
Methanedicarboxylic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.003 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 104.061 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.619 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 135 to 137 °C (275 to 279 °F; 408 to 410 K) (decomposes) |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
| 763 g/L | |
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa1 = 2.83[2] pKa2 = 5.69[2] |
| -46.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Malonate |
Related carboxylic acids
|
Oxalic acid Propionic acid Succinic acid Fumaric acid |
Related compounds
|
Malondialdehyde Dimethyl malonate |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
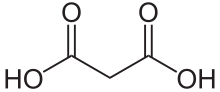
Malonic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with structure CH2(COOH)2. The ionized form of malonic acid, as well as its esters and salts, are known as malonates. For example, diethyl malonate is malonic acid's diethyl ester. The name originates from the Greek word μᾶλον (malon) meaning 'apple'.
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 746. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b pKa Data Compiled by R. Williams (pdf; 77 kB) Archived 2010-06-02 at the Wayback Machine