
Back Bahsa Mandarin ACE Mandaryns Afrikaans Nordchinesische Dialekte ALS Chinés mandarín AN मंदारिन चीनी ANP ماندراين الصينية Arabic ܠܫܢܐ ܡܢܕܪܝܢܝܐ ARC Chinu mandarín AST Mandarin çincəsi Azerbaijani Basa Mandarin BAN
| Mandarin | |
|---|---|
| 官话; 官話 (Guānhuà) | |
 | |
| Native to | China |
| Region | North China, Central China, Southwestern China |
| Speakers | L1: 940 million (2021)[1] L2: 200 million (no date)[1] Total: 1.1 billion (2021)[1] |
Early forms | |
Standard forms |
|
| Varieties | |
| Chinese Sign Language[2] | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | cmn |
| Glottolog | mand1415 |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA-b |
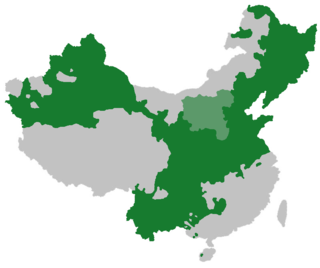 Mandarin area in China as of 1987, including Sichuanese, Lower Yangtze and (in light green) Jin, which are arguably separate languages | |
 Countries and regions where Mandarin is spoken as L1 or L2
Majority native language
Statutory or de facto national working language
More than 1,000,000 speakers
More than 500,000 speakers
More than 100,000 speakers | |
| Mandarin Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 官话 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 官話 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Officials' speech | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Northern Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 北方话 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 北方話 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Northern speech | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Mandarin (/ˈmændərɪn/ ⓘ MAN-dər-in; simplified Chinese: 官话; traditional Chinese: 官話; pinyin: Guānhuà; lit. 'officials' speech') is the largest branch of the Sinitic languages. Mandarin varieties are spoken by 70 percent of all Chinese speakers over a large geographical area that stretches from Yunnan in the southwest to Xinjiang in the northwest and Heilongjiang in the northeast. Its spread is generally attributed to the greater ease of travel and communication in the North China Plain compared to the more mountainous south, combined with the relatively recent spread of Mandarin to frontier areas.
Many varieties of Mandarin, such as those of the Southwest (including Sichuanese) and the Lower Yangtze, are not mutually intelligible with the Beijing dialect (or are only partially intelligible). Nevertheless, Mandarin as a group is often placed first in lists of languages by number of native speakers (with nearly one billion). Because Mandarin originated in North China and most Mandarin varieties are found in the north, the group is sometimes referred to as Northern Chinese (simplified Chinese: 北方话; traditional Chinese: 北方話; pinyin: Běifānghuà; lit. 'northern speech').
Most Mandarin varieties have four tones. The final stops of Middle Chinese have disappeared in most of these varieties, but some have merged them as a final glottal stop. Many Mandarin varieties, including that of Beijing, retain retroflex initial consonants, which have been lost in southern Chinese languages.
The capitals of China have been within the Mandarin-speaking area for most of the last millennium, making these dialects very influential. Some form of Mandarin has served as a lingua franca for government officials and the courts since the 14th century.[3] In the early 20th century, a standard form based on the Beijing dialect, with elements from other Mandarin varieties, was adopted as the national language. Standard Chinese is the official language of China[4] and Taiwan,[5] one of four official languages of Singapore and one of six official languages of the United Nations.[6] Recent increased migration from Mandarin-speaking regions of China and Taiwan has now resulted in the language being one of the more frequently used varieties of Chinese among Chinese diaspora communities. It is also the most commonly taught Chinese language.
- ^ a b c Mandarin at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)

- ^ 台灣手語簡介 (Taiwan shouyu jianjie) (2009)
- ^ Norman (1988), p. 136.
- ^ "Law of the People's Republic of China on the Standard Spoken and Written Chinese Language (Order of the President No.37)". Chinese Government. 31 October 2000. Archived from the original on 24 July 2013. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
For purposes of this Law, the standard spoken and written Chinese language means Putonghua (a common speech with pronunciation based on the Beijing dialect) and the standardized Chinese characters.
- ^ "ROC Vital Information". Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of China (Taiwan). 31 December 2014. Archived from the original on 2 May 2017. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ^ 《人民日报》评论员文章:说普通话 用规范字. www.gov.cn (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 20 February 2018. Retrieved 26 July 2017.