
Back Britse mandaat van Palestina Afrikaans Palestine þæt Brittisce Gebodrīce ANG الانتداب البريطاني على فلسطين Arabic الانتداب البريطانى على فلسطين ARZ Mandatu Británicu de Palestina AST Fələstin mandatlığı Azerbaijani بیرلشیک کراللیک فیلیسطین مانداسی AZB Брытанскі мандат у Палесціне Byelorussian Брытанскі мандат у Палестыне BE-X-OLD Подмандатна Палестина Bulgarian
Palestine | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1920–1948 | |||||||||||||
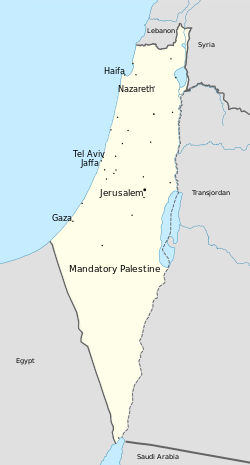 Mandatory Palestine in 1946 | |||||||||||||
| Status | Mandate of the United Kingdom | ||||||||||||
| Capital | Jerusalem | ||||||||||||
| Common languages | Arabic, English, Hebrew | ||||||||||||
| Religion (1922)[2] | 78% Islam 11% Judaism 10% Christianity 1% other including Baháʼí Faith, Druze faith | ||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Palestinian | ||||||||||||
| High Commissioner | |||||||||||||
• 1920–1925 (first) | Sir Herbert L. Samuel | ||||||||||||
• 1945–1948 (last) | Sir Alan Cunningham | ||||||||||||
| Legislature | |||||||||||||
• Parliamentary body of the Muslim community | Supreme Muslim Council | ||||||||||||
• Parliamentary body of the Jewish community | Assembly of Representatives | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | |||||||||||||
• Mandate assigned | 25 April 1920 | ||||||||||||
• Britain officially assumes control | 29 September 1923 | ||||||||||||
| 14 May 1948 | |||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||
• Total | 25,585.3 km2 (9,878.5 sq mi)[3] | ||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||
• Census | 757,182 (1922)[4] | ||||||||||||
| Currency | Egyptian pound (until 1927) Palestine pound (from 1927) | ||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | PS | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Today part of | Israel Palestine | ||||||||||||
Mandatory Palestine[a][5] was a geopolitical entity that existed between 1920 and 1948 in the region of Palestine under the terms of the League of Nations Mandate for Palestine.
After an Arab uprising against the Ottoman Empire during the First World War in 1916, British forces drove Ottoman forces out of the Levant.[6] The United Kingdom had agreed in the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence that it would honour Arab independence in case of a revolt but, in the end, the United Kingdom and France divided what had been Ottoman Syria under the Sykes–Picot Agreement—an act of betrayal in the eyes of the Arabs. Another issue was the Balfour Declaration of 1917, in which Britain promised its support for the establishment of a Jewish "national home" in Palestine. Mandatory Palestine was then established in 1920, and the British obtained a Mandate for Palestine from the League of Nations in 1922.[7]
During the Mandate, the area saw successive waves of Jewish immigration and the rise of nationalist movements in both the Jewish and Arab communities. Competing interests of the two populations led to the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine and the 1944–1948 Jewish insurgency in Mandatory Palestine. The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine to divide the territory into two states, one Arab and one Jewish, was passed in November 1947. The 1948 Palestine war ended with the territory of Mandatory Palestine divided among the State of Israel, the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, which annexed territory on the West Bank of the Jordan River, and the Kingdom of Egypt, which established the "All-Palestine Protectorate" in the Gaza Strip.
Mandatory Palestine was designated as a Class A Mandate, based on its social, political, and economic development. This classification was reserved for post-war mandates with the highest capacity for self-governance.[8] All Class A mandates other than mandatory Palestine had gained independence by 1946.[9]
- ^ "Palestine seal". www.royalmintmuseum.org.uk. Retrieved 12 February 2024.
- ^ ""Hope Simpson report, Chapter III". Zionism-israel.com. October 1930.
- ^ Department of Statistics (1945). Village Statistics, April, 1945. Government of Palestine. Scan of the original document at the National Library of Israel.
- ^ 1922 Census of Palestine, retrieved 19 February 2024.
- ^ "League of Nations decision confirming the Principal Allied Powers' agreement on the territory of Palestine". Archived from the original on 25 November 2013.
- ^ Hughes, Matthew, ed. (2004). Allenby in Palestine: The Middle East Correspondence of Field Marshal Viscount Allenby June 1917 – October 1919. Army Records Society. Vol. 22. Phoenix Mill, Thrupp, Stroud, Gloucestershire: Sutton Publishing Ltd. ISBN 978-0-7509-3841-9. Allenby to Robertson 25 January 1918 in Hughes 2004, p. 128
- ^ Article 22, The Covenant of the League of Nations Archived 26 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine and "Mandate for Palestine", Encyclopaedia Judaica, Vol. 11, p. 862, Keter Publishing House, Jerusalem, 1972
- ^ Legal Consequences of the Construction of a Wall in the Occupied Palestinian Territory, Advisory Opinion of 9 July 2004, 2004 International Court of Justice 63.
- ^ Victor Kattan. From Coexistence to Conquest, International Law and the Origins of the Arab-Israeli Conflict, 1891–1949. London, New York: Pluto Press, 2009.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).

![Public Seal[1] of Palestine](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/22/Public_Seal_of_Mandatory_Palestine.png/85px-Public_Seal_of_Mandatory_Palestine.png)