
Back Мінская аперацыя Byelorussian Менская апэрацыя BE-X-OLD Batalo de Minsko Esperanto Minskin offensiivi Finnish Offensive de Minsk French Minskoffensief Dutch Operacja mińska Polish Минская операция Russian Minsk Taarruzu Turkish Мінська операція Ukrainian
| Minsk offensive | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Operation Bagration | |||||||
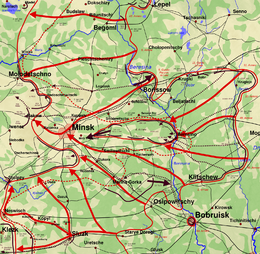 Map of the Minsk offensive | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
(Army Group Centre) (elements of Fourth Army) |
(3rd Belorussian Front) (1st Belorussian Front) (2nd Belorussian Front) (1st Baltic Front) | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
100,000 troops caught in encirclement (40,000 killed or missing, rest either wounded or captured) | Unknown | ||||||
The Minsk offensive (Russian: Минская наступательная операция) was part of the second phase of the Belorussian strategic offensive of the Red Army in summer 1944, commonly known as Operation Bagration.
The Red Army encircled the German Fourth Army in the city of Minsk. Hitler ordered the Fourth Army to hold fast, declaring the city to be a fortified place (fester Platz) and defended even if encircled. The Soviet 5th Guards Tank Army attacked from the north-east, while the 2nd Guards Tank Corps moved in from the east, and the 65th Army advanced from the south. About 100,000 Axis soldiers from the Fourth and Ninth Armies were encircled, of whom some 40,000 were killed and most of the rest captured. The result was a complete victory for the Red Army, the liberation of Minsk, and the rapid destruction of much of the German Army Group Centre.