
Back حبل ظهري Arabic Хорда (заалогія) Byelorussian Хорда (заалёгія) BE-X-OLD नोटोकॉर्ड Bihari নটোকর্ড Bengali/Bangla Notohord BS Notocordi Catalan Struna hřbetní Czech Хирлӳ (зоологи) CV Chorda dorsalis German
This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. (February 2017) |
| Notochord | |
|---|---|
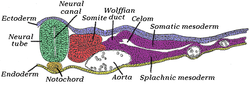 Transverse section of a chick embryo of forty-five hours' incubation. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Axial mesoderm |
| Gives rise to | Nucleus pulposus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | notochorda |
| MeSH | D009672 |
| TE | E5.0.1.1.0.0.8 |
| FMA | 85521 |
| Anatomical terminology | |

The notochord is an elastic, rod-like structure found in chordates. In chordate vertebrates the notochord is an embryonic structure that disintegrates, as the vertebrae develop, to become the nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral discs of the vertebral column. In non-vertebrate chordates a notochord persists.
The notochord is derived from the embryonic mesoderm and consists of an inner core of vacuolated cells filled with glycoproteins, covered by two helical collagen-elastin sheaths. It lies longitudinally along the rostral-caudal (head to tail) axis of the body, dorsal to the gut tube, and ventral to the dorsal nerve cord. Some chordate invertebrates, such as tunicates, develop a notochord during the larval stage but lose it through subsequent stages into adulthood.
The notochord is important for signaling the dorso-ventral patterning of cells coming from the mesodermal progenitors. This helps form the precursors needed for certain organs and the embryo to develop. In summary, the notochord plays essential roles in embryonic development.
The notochord provides a directional reference to the surrounding tissue as a midline structure during embryonic development, acts as a precursor for vertebrae and a primitive axial endoskeleton. In aquatic animals it can facilitate tail motion when swimming.[1]
- ^ Schifferl, D., Scholze-Wittler, M., Villaronga Luque, A., Pustet, M., Wittler, L., Veenvliet, J. V., Koch, F., & Herrmann, B. G. (2023). Genome-wide identification of notochord enhancers comprising the regulatory landscape of the brachyury locus in mouse. Development (Cambridge, England), 150(22). https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.202111