
Back Kernreaksie Afrikaans تفاعل نووي Arabic تفاعل نووي ARY Nüvə reaksiyası Azerbaijani Ядзерная рэакцыя Byelorussian Ядрена реакция Bulgarian পারমাণবিক বিক্রিয়া Bengali/Bangla Reacció nuclear Catalan Hŏk huāng-éng CDO کاردانەوەی ناوکی CKB

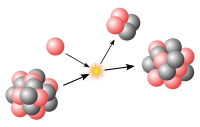
3Li
) and deuterium (2
1H
) react to form the highly excited intermediate nucleus 8
4Be
which then decays immediately into two alpha particles of helium-4 (4
2He
). Protons are symbolically represented by red spheres, and neutrons by blue spheres.
| Nuclear physics |
|---|
 |
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another. If a nucleus interacts with another nucleus or particle, they then separate without changing the nature of any nuclide, the process is simply referred to as a type of nuclear scattering, rather than a nuclear reaction.
In principle, a reaction can involve more than two particles colliding, but because the probability of three or more nuclei to meet at the same time at the same place is much less than for two nuclei, such an event is exceptionally rare (see triple alpha process for an example very close to a three-body nuclear reaction). The term "nuclear reaction" may refer either to a change in a nuclide induced by collision with another particle or to a spontaneous change of a nuclide without collision.
Natural nuclear reactions occur in the interaction between cosmic rays and matter, and nuclear reactions can be employed artificially to obtain nuclear energy, at an adjustable rate, on-demand. Nuclear chain reactions in fissionable materials produce induced nuclear fission. Various nuclear fusion reactions of light elements power the energy production of the Sun and stars.