
Back عضلة سدادية غائرة Arabic Múscul obturador intern Catalan Musculus obturator internus German Músculo obturador interno Spanish ماهیچه سدادی درونی Persian Muscle obturateur interne French השריר הסותם הפנימי HE Nutarnji zaptivni mišić Croatian Muscolo otturatore interno Italian 内閉鎖筋 Japanese
| Internal obturator muscle | |
|---|---|
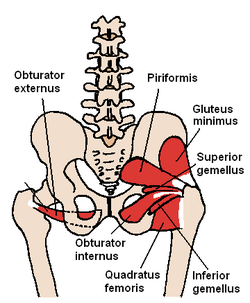 The obturator internus and nearby muscles (posterior view) | |
 Coronal section of anterior part of pelvis, through the pubic arch. Seen from in front. (Obturator internus labeled at right.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Ischiopubic ramus and obturator membrane |
| Insertion | Medial aspect of the greater trochanter |
| Artery | Inferior gluteal artery |
| Nerve | Nerve to obturator internus (L5, S1, S2) |
| Actions | Abducts and laterally rotates the extended hip and abducts the flexed thigh at the hip, and stabilizes the hip during walking |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus obturatorius internus |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.012 |
| TA2 | 2605 |
| FMA | 22298 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The internal obturator muscle or obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis.
It exits the pelvic cavity through the lesser sciatic foramen.
The internal obturator is situated partly within the lesser pelvis, and partly at the back of the hip-joint.
It functions to help laterally rotate femur with hip extension and abduct femur with hip flexion, as well as to steady the femoral head in the acetabulum.