Back Eerste Babiloniese dinastie Afrikaans السلالة البابلية الأولى Arabic Dinasti Babilonia Partama BJN পুরাতন ব্যাবিলনীয় সাম্রাজ্য Bengali/Bangla Imperi paleobabilònic Catalan یەکەمین ئیمپراتۆریەتیی بابلی CKB Starobabylonské období Czech Imperio paleobabilónico Spanish امپراتوری بابل کهن Persian Babylonian ensimmäinen dynastia Finnish
Old Babylonian Empire | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 1894 BC – c. 1595 BC | |||||||||||
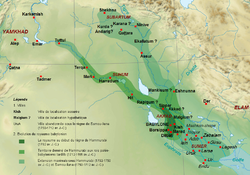 | |||||||||||
| Capital | Babylon | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Akkadian (official), Sumerian (literary), Amorite | ||||||||||
| Religion | Babylonian religion | ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| King | |||||||||||
• c. 1894–1881 BC | Sumu-abum (first) | ||||||||||
• c. 1792–1750 BC | Hammurabi | ||||||||||
• c. 1626–1595 BC | Samsu-Ditana (last) | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Bronze Age | ||||||||||
• Established | c. 1894 BC | ||||||||||
| c. 1595 BC | |||||||||||
• Disestablished | c. 1595 BC | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Iraq Syria | ||||||||||
The Old Babylonian Empire, or First Babylonian Empire, is dated to c. 1894–1595 BC, and comes after the end of Sumerian power with the destruction of the Third Dynasty of Ur, and the subsequent Isin-Larsa period. The chronology of the first dynasty of Babylonia is debated; there is a Babylonian King List A[1] and also a Babylonian King List B, with generally longer regnal lengths.[2] In this chronology, the regnal years of List A are used due to their wide usage.