
Back طب العيون في عصر الحضارة الإسلامية Arabic মধ্যযুগীয় ইসলামে চক্ষুরোগ-চিকিৎসা Bengali/Bangla چشمپزشکی در عصر تمدن اسلامی Persian Ophthalmologie dans la civilisation islamique médiévale French
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2007) |
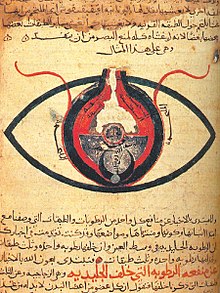
Ophthalmology was one of the foremost branches in medieval Islamic medicine. The oculist or kahhal (کحال), a somewhat despised professional in Galen's time, was an honored member of the medical profession by the Abbasid period, occupying a unique place in royal households. Medieval Islamic scientists (unlike their classical predecessors) considered it normal to combine theory and practice, including the crafting of precise instruments, and therefore found it natural to combine the study of the eye with the practical application of that knowledge.[1] The specialized instruments used in their operations ran into scores. Innovations such as the "injection syringe", a hollow needle, invented by Ammar ibn Ali of Mosul, which was used for the extraction by suction of soft cataracts, were quite common.
Muslim physicians described such conditions as pannus, glaucoma (described as "headache of the pupil"), phlyctenulae, and operations on the conjunctiva. They were the first to use the words "retina" and "cataract".
- ^ David C. Lindberg (1980), Science in the Middle Ages, University of Chicago Press, p. 21, ISBN 0-226-48233-2