
Back إعطاء فموي Arabic মৌখিক ব্যবস্থাপনা Bengali/Bangla Oralna primjena BS Via oral Catalan دەرمان لە ڕێگەی دەم CKB Perorální podání Czech Peroral administration Danish Peroral German Administración oral Spanish تجویز دهانی دارو Persian
| Oral administration | |
|---|---|
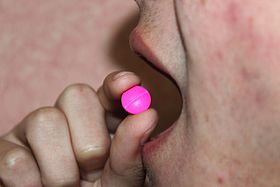 Oral administration of a tablet | |
| Other names | By mouth, per os (PO) |


Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications.
Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow.[1]
- ^ "Oral Administration of Drugs: Advantages and Disadvantages". Retrieved December 8, 2022.