
Back Parlement van Kanada Afrikaans Canadan Witenagemot ANG البرلمان الكندي Arabic برلمان كندا ARZ Parllamentu de Canadá AST Парламент Канады Byelorussian Парламент на Канада Bulgarian কানাডীয় সংসদ Bengali/Bangla Parlament del Canadà Catalan Канада парламенчĕ CV
Parliament of Canada Parlement du Canada | |
|---|---|
| 44th Parliament | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | |
| History | |
| Founded | 1 July 1867 |
| Preceded by | Initially assumed some jurisdiction from:
Later added some jurisdiction from: |
| Leadership | |
Charles III since 8 September 2022 | |
Mary Simon since 26 July 2021 | |
| Structure | |
| Seats |
|
 | |
Senate political groups |
Conservative (15)
Non-affiliated (10)
Vacant (10) |
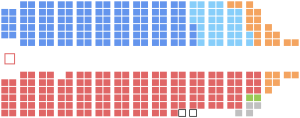 | |
House of Commons political groups | His Majesty's Government
His Majesty's Loyal Opposition
Parties without official status
|
| Elections | |
| Appointment by the governor general on advice of the prime minister | |
| First-past-the-post | |
Last House of Commons election | 20 September 2021 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| |
| Website | |
| parl | |
The Parliament of Canada (French: Parlement du Canada) is the federal legislature of Canada, seated at Parliament Hill in Ottawa, and is composed of three parts: the King, the Senate, and the House of Commons.[2] By constitutional convention, the House of Commons is dominant, with the Senate rarely opposing its will. The Senate reviews legislation from a less partisan standpoint and may initiate certain bills. The monarch or his representative, normally the governor general, provides royal assent to make bills into law. According to Section 16 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, the official languages of the parliament are English and French.[3]
The governor general, on behalf of the monarch, summons and appoints the 105 senators on the advice of the prime minister, while each of the 338 members of the House of Commons – called members of Parliament (MPs) – represents an electoral district, commonly referred to as a riding, and are elected by Canadian voters residing in the riding. The governor general also summons and calls together the House of Commons, and may prorogue or dissolve Parliament, in order to either end a parliamentary session or call a general election. The governor general also delivers the throne speech at the opening of each new Parliament (the monarch occasionally has done so, instead of the governor general, when visiting Canada).
The current Parliament, summoned by Governor General Mary Simon in November 2021, is the 44th Parliament since Confederation in 1867. On January 6, 2025, the Parliament was prorogued by Simon following prime minister Justin Trudeau's request to do so and will remain suspended until March 24.[4]
- ^ Honderich, Holly. "Canada's NDP pulls support for Trudeau's Liberals". bbc.com. British Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- ^ Constitution Act, 1867, s. 17.
- ^ "CONSTITUTION ACT, 1982". laws-lois.justice.gc.ca. Government of Canada. Retrieved 7 January 2025.
- ^ Maimann, Kevin; Schmunk, Rhianna (6 January 2025). "Canadian Parliament is prorogued. Here's what that means". CBC.ca. Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC). Retrieved 7 January 2025.