
Back Perifere senuweestelsel Afrikaans جهاز عصبي محيطي Arabic ܬܘܩܢ ܓܝܕܝܐ ܡܚܕܘܪܝܐ ARC Sistema nerviosu periféricu AST Periferik sinir sistemi Azerbaijani Периферна нервна система Bulgarian প্রান্তীয় স্নায়ুতন্ত্র Bengali/Bangla Periferni nervni sistem BS Sistema nerviós perifèric Catalan کۆئەندامی پەییی دەوروبەری CKB
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2020) |
| Peripheral nervous system | |
|---|---|
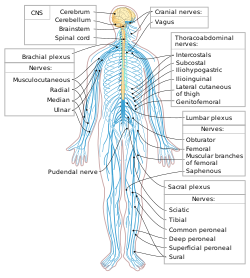 The human nervous system. Sky blue is PNS; yellow is CNS. | |
| Identifiers | |
| Acronym(s) | PNS |
| MeSH | D017933 |
| TA98 | A14.2.00.001 |
| TA2 | 6129 |
| FMA | 9093 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain and the spinal cord.[1] The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body.[2] Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins.[3]
The peripheral nervous system can be divided into the somatic nervous system and the visceral nervous system. Each of these have a sensory and a motor division. The visceral motor division is known as the autonomic nervous system.[4] In the somatic nervous system, the cranial nerves are part of the PNS with the exceptions of the olfactory nerve and epithelia and the optic nerve (cranial nerve II) along with the retina, which are considered parts of the central nervous system based on developmental origin. The second cranial nerve is not a true peripheral nerve but a tract of the diencephalon.[5] Cranial nerve ganglia, as with all ganglia, are part of the PNS.[6] The autonomic nervous system exerts involuntary control over smooth muscle and glands.[7] The connection between CNS and organs allows the system to be in two different functional states: sympathetic and parasympathetic.
- ^ Alberts, Daniel (2012). Dorland's illustrated medical dictionary (32nd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier. p. 1862. ISBN 9781416062578.
- ^ "Slide show: How your brain works - Mayo Clinic". mayoclinic.com. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^ Aspromonte, John (2019). ADHD : the ultimate teen guide. Lanham. p. 51. ISBN 978-1-5381-0039-4. OCLC 1048014796.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Saladin, Kenneth (2024). Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function (10th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw Hill. p. 1076. ISBN 9781266041846.
- ^ Board Review Series: Neuroanatomy, 4th Ed., Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Maryland 2008, p. 177. ISBN 978-0-7817-7245-7.
- ^ James S. White (21 March 2008). Neurobioscitifity. McGraw-Hill Professional. pp. 1–. ISBN 978-0-07-149623-0. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ^ Campbell biology. Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven Alexander Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Rebecca B. Orr, Neil A. Campbell (12th ed.). New York, NY. 2021. ISBN 978-0-13-518874-3. OCLC 1119065904.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link)