
Back التهاب البلعوم Arabic Faringit Azerbaijani Фарынгіт Byelorussian গলবিল প্রদাহ Bengali/Bangla Faringitis Catalan Faryngitida Czech Dolur gwddw Welsh Svælgkatar Danish Pharyngitis German އަރުތެރެ ދުޅަވުން DV
| Pharyngitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Acute sore throat |
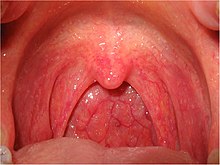 | |
| Viral pharyngitis resulting in visible redness. | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Sore throat, fever, runny nose, cough, headache, hoarse voice[1][2] |
| Complications | Sinusitis, acute otitis media[2] |
| Duration | 3–10 days, depending on cause[2][3] |
| Causes | Usually viral infection[2] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, rapid antigen detection test, throat swab[2] |
| Differential diagnosis | Epiglottitis, thyroiditis, retropharyngeal abscess[2] |
| Treatment | lidocaine[2][4] |
| Frequency | ~7.5% of people in any 3-month period[5] |
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx.[2] It typically results in a sore throat and fever.[2] Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, difficulty swallowing, swollen lymph nodes, and a hoarse voice.[1][6] Symptoms usually last 3–5 days, but can be longer depending on cause.[2][3] Complications can include sinusitis and acute otitis media.[2] Pharyngitis is a type of upper respiratory tract infection.[7]
Most cases are caused by a viral infection.[2] Strep throat, a bacterial infection, is the cause in about 25% of children and 10% of adults.[2] Uncommon causes include other bacteria such as gonococcus, fungi, irritants such as smoke, allergies, and gastroesophageal reflux disease.[2][4] Specific testing is not recommended in people who have clear symptoms of a viral infection, such as a cold.[2] Otherwise, a rapid antigen detection test or throat swab is recommended.[2] PCR testing has become common as it is as good as taking a throat swab but gives a faster result.[8] Other conditions that can produce similar symptoms include epiglottitis, thyroiditis, retropharyngeal abscess, and occasionally heart disease.[2]
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, can be used to help with the pain.[2] Numbing medication, such as topical lidocaine, may also help.[4] Strep throat is typically treated with antibiotics, such as either penicillin or amoxicillin.[2] It is unclear whether steroids are useful in acute pharyngitis, other than possibly in severe cases, but a recent (2020) review found that when used in combination with antibiotics they moderately reduced pain and the likelihood of resolution.[9][10]
About 7.5% of people have a sore throat in any 3-month period.[5] Two or three episodes in a year are not uncommon.[1] This resulted in 15 million physician visits in the United States in 2007.[4] Pharyngitis is the most common cause of a sore throat.[11] The word comes from the Greek word pharynx meaning "throat" and the suffix -itis meaning "inflammation".[12][13]
- ^ a b c Rutter, Paul Professor; Newby, David (2015). Community Pharmacy ANZ: Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 19. ISBN 9780729583459. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Hildreth, AF; Takhar, S; Clark, MA; Hatten, B (September 2015). "Evidence-Based Evaluation And Management Of Patients With Pharyngitis In The Emergency Department". Emergency Medicine Practice. 17 (9): 1–16, quiz 16–7. PMID 26276908.
- ^ a b David A.Warrell; Timothy M. Cox; John D. Firth, eds. (2012). Oxford textbook of medicine infection. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 280–281. ISBN 9780191631733. Archived from the original on 10 October 2016.
- ^ a b c d Weber, R (March 2014). "Pharyngitis". Primary Care. 41 (1): 91–8. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2013.10.010. PMC 7119355. PMID 24439883.
- ^ a b Jones, Roger (2004). Oxford Textbook of Primary Medical Care. Oxford University Press. p. 674. ISBN 9780198567820. Retrieved 4 August 2016.
- ^ Neville, Brad W.; Damm, Douglas D.; Allen, Carl M.; Chi, Angela C. (2016). Oral and maxillofacial pathology (4th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Elsevier. p. 166. ISBN 9781455770526. OCLC 908336985. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- ^ "Pharyngitis". National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 20 May 2016. Retrieved 4 August 2016.
- ^ "Acute pharyngitis - Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment | BMJ Best Practice". bestpractice.bmj.com.
- ^ Principi, N; Bianchini, S; Baggi, E; Esposito, S (February 2013). "No evidence for the effectiveness of systemic corticosteroids in acute pharyngitis, community-acquired pneumonia and acute otitis media". European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. 32 (2): 151–60. doi:10.1007/s10096-012-1747-y. PMC 7087613. PMID 22993127.
- ^ de Cassan, Simone; Thompson, Matthew J.; Perera, Rafael; Glasziou, Paul P.; Del Mar, Chris B.; Heneghan, Carl J.; Hayward, Gail (1 May 2020). "Corticosteroids as standalone or add-on treatment for sore throat". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020 (5): CD008268. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008268.pub3. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 7193118. PMID 32356360.
- ^ Marx, John (2010). Rosen's emergency medicine: concepts and clinical practice (7th ed.). Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Mosby/Elsevier. Chapter 30. ISBN 978-0-323-05472-0.
- ^ Beachey, Will (2013). Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology, Foundations for Clinical Practice,3: Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 5. ISBN 978-0323078665. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- ^ Hegner, Barbara; Acello, Barbara; Caldwell, Esther (2009). Nursing Assistant: A Nursing Process Approach – Basics. Cengage Learning. p. 45. ISBN 9781111780500. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.