| Part of a series on |
| Microbiomes |
|---|
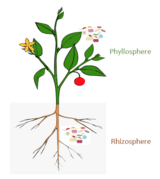 |
Since the colonization of land by ancestral plant lineages 450 million years ago, plants and their associated microbes have been interacting with each other, forming an assemblage of species that is often referred to as a holobiont. Selective pressure acting on holobiont components has likely shaped plant-associated microbial communities and selected for host-adapted microorganisms that impact plant fitness. However, the high microbial densities detected on plant tissues, together with the fast generation time of microbes and their more ancient origin compared to their host, suggest that microbe-microbe interactions are also important selective forces sculpting complex microbial assemblages in the phyllosphere, rhizosphere, and plant endosphere compartments.[1]
- ^ Hassani MA, Durán P, Hacquard S (March 2018). "Microbial interactions within the plant holobiont". Microbiome. 6 (1): 58. doi:10.1186/s40168-018-0445-0. PMC 5870681. PMID 29587885.
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
