Introduction
Football is the most popular sport in Africa, alongside basketball. Indeed, football is probably the most popular sport in almost every African country, although rugby and cricket are also very popular in South Africa. The first football stadium to be built in Africa was the Alexandria Stadium in 1929.
The English Premier League is the most popular sports league in Africa. The most popular clubs in Africa are Arsenal, Chelsea and Manchester United. (Full article...)
This section may be unbalanced toward certain viewpoints. (October 2022) |

Selected article -
Selected biography -
Enyeama began his career with Enyimba, with whom he won the CAF Champions League twice. After three seasons with Enyimba and one with Iwuanyanwu Nationale (now known as Heartland), Enyeama moved to Bnei Yehuda Tel Aviv in Israel. In his first season at the club, the team qualified for the final of the Israel State Cup and achieved fourth place in the Israeli Premier League, which qualified the team for the UEFA Cup.
Enyeama signed for Hapoel Tel Aviv in 2007, helped the team avoid relegation and reach the state cup final during a poor 2007–08 season. He won the "Player of The Year" award in 2008–09, and in 2009–10 Hapoel won the double. On 18 August 2010 he scored his first goal of the 2010–11 season with a penalty against Red Bull Salzburg in the Champions League qualifiers.
In June 2011, Enyeama moved to Lille in the French Ligue 1 for an undisclosed fee on a three-year contract. He made his debut on 18 October 2011 against Inter Milan in the 2012 UEFA Champions League group stage, where Inter managed a 1–0 victory. In August 2012, Enyeama agreed a one-year loan deal with Maccabi Tel Aviv and was presented to the media by Maccabi's Sports Director Jordi Cruyff at 8 August 2012. Upon his return to Lille, club manager René Girard picked Enyeama as his first-choice goalkeeper ahead of Steeve Elana, who had been the first-choice goalkeeper when Rudi Garcia was the club manager.
Selected image -
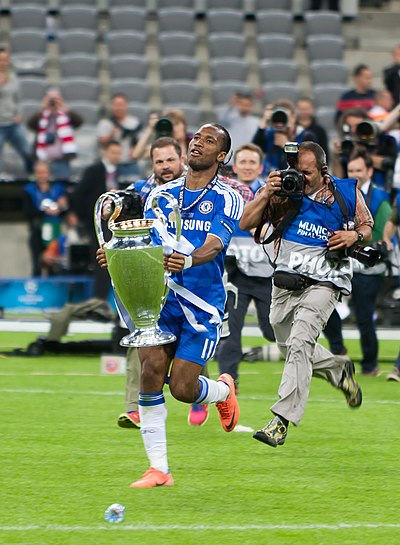 |
Didier Drogba holding the European Cup following Chelsea's penalty shootout victory over Bayern Munich
Subcategories
Related portals
More sports portals
WikiProjects
Related task forces and sub-projects
African football task force
WikiProject Africa • WikiProject Football
WikiProject Football task forces and sub-projects
 | |
| Wikipedia ads | file info – #250 |
Topics
Open tasks

- Expand stubs: Competitions in Africa • Organizations
- Expand club articles of teams from Africa.
- Expand biographies of Africans involved in football.
- Create: Requested articles • Most wanted football articles • Requested general football articles
- Add: Infoboxes • Images (General requests, Requested images of people)
- Review: articles currently under review
- Assess: Assessment requests • Assess an article
- Revert vandalism on this portal and on African football articles
- Assist in maintaining this portal and keeping its selected content up to date.
- WikiNews: Create and submit news stories about African football for Wikipedia's sister project WikiNews.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
More portals
Sources

- ^ "The History Of Soccer In Africa". NPR.org. 2010-06-09. Retrieved 2016-03-31.
- ^ a b c Alegi, Peter (2010). African Soccerscapes. Ohio University Press. pp. 1–2. ISBN 9780896802780.
- ^ Frimpong, Enoch Darfah. "Ghana news: A world of superstition, frustration and disillusionment - Graphic Online". Retrieved 23 September 2017.
- ^ Lacey, Marc (8 August 2002). "Kangemi Journal; For Spellbinding Soccer, the Juju Man's on the Ball". The New York Times. NY Times. Retrieved 2016-03-31.
- ^ "World Cup Witchcraft: Africa Teams Turn to Magic for Aid". National Geographic. Archived from the original on July 10, 2006. Retrieved 2016-03-31.
- ^ Andy Mitten (September 2010). The Rough Guide to Cult Football. Rough Guides UK. ISBN 9781405387965. Retrieved 2016-04-02.
- ^ "African Nations Cup overshadowed by hocus pocus | Football". The Guardian. Retrieved 2016-04-09.
- ^ Kuper, Simon (2006). Soccer Against the Enemy: How the World's Most Popular Sport Starts and Stops Wars, Fuels Revolutions, and Keeps Dictators in Power. Nation Books. p. 123. ISBN 978-1-56025-878-0.