Back بوابة:المجر Arabic Portal:Macarıstan Azerbaijani Portál:Maďarsko Czech Portal:Ungarn German Portal:Hungría Spanish Portail:Hongrie French Portal:Hungría Galician Portál:Magyarország Hungarian Portale:Ungheria Italian Porta:Hungaria Latin
The Hungary Portal




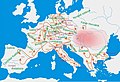
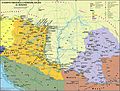
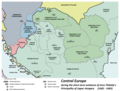
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary lies within the drainage basin of the Danube River and is dominated by great lowland plains. It has a population of 9.5 million, comprised mostly of ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani minority. Hungarian is the official language, and among the few in Europe outside the Indo-European family. Budapest is the country's capital and largest city, and the dominant cultural and economic centre.
Prior to the foundation of the Hungarian state, various peoples settled in the territory of present-day Hungary, including the Celts, Romans, Huns, Germanic peoples, Avars and Slavs. Hungarian statehood is traced to the Principality of Hungary, which was established in the late ninth century by Álmos and his son Árpád through the conquest of the Carpathian Basin. King Stephen I ascended the throne in 1000 and converted his realm to a Christian kingdom. The medieval Kingdom of Hungary was a European power, reaching its height in the Late Middle Ages.
After a long period of Ottoman wars, Hungary’s forces were defeated at the Battle of Mohács in 1526 and its capital Buda was captured in 1541, opening a period of more than 150 years where the country was divided into three parts: Royal Hungary (loyal to the Habsburgs), Ottoman Hungary and the largely independent Principality of Transylvania. The Ottomans recognized the loss of Ottoman Hungary by the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. Most of Hungary was reunited and came under Habsburg rule by the turn of the 18th century.
Wars of independence against the Habsburgs in 1703–1711 and 1848–1849 resulted in a compromise that established the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy in 1867, a major power in the early 20th century. Austria-Hungary collapsed after World War I, and the subsequent Treaty of Trianon in 1920 established Hungary's current borders, resulting in the loss of 71% of its historical territory, majority of its economy, 58% of its population, and 32% of its ethnic Hungarians.
Reeling from the aftermath of the war, Hungary endured turmoil in the early interwar period, culminating in the nationalist conservative regime of de facto ruler Miklós Horthy. Hungary joined the Axis powers in World War II, suffering significant damage and casualties. It was occupied by the Soviet Union, which established the Hungarian People's Republic as a satellite state. Following the failed 1956 revolution, Hungary became comparatively freer but remained a repressed member of the Eastern Bloc. As part of the Revolutions of 1989, Hungary peacefully transitioned into a democratic parliamentary republic. It joined the European Union in 2004 and the Schengen Area since 2007. Since the election of Viktor Orbán in 2010, Hungary has undergone democratic backsliding and become an illiberal democracy and hybrid regime.
Hungary is a high-income economy with universal health care and tuition-free secondary education. Hungary has a long history of significant contributions to arts, music, literature, sports, science and technology. It is a popular tourist destination in Europe, drawing 24.5 million international visitors in 2019. Hungary is a member of numerous international organisations, including the Council of Europe, European Union, NATO, United Nations, World Health Organization, World Trade Organization, World Bank, Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, and the Visegrád Group. (Full article...)
Turk or Turks may refer to: (Full article...)
Selected article -

The iconostasis of the Cathedral of Hajdúdorog is the largest Greek Catholic icon screen in Hungary. It is 11 m (36 ft.) tall and 7 m (23 ft.) wide, holding 54 icons on five tiers. Creating such a monumental work of art requires a number of different craftsmen. Miklós Jankovits was hired by the Greek Catholic parish of Hajdúdorog in 1799 to carve the wooden framework, including the doors and the icon frames of the iconostasis. Mátyás Hittner and János Szűts could only start the painting and gilding works in 1808. The last icon was completed in 1816.
The icons were painted clearly in Western style, quite unusual in Eastern rite churches. Instead of the traditional Byzantine iconographic depiction, the painters used the deep, rich colors, the intense light and dark shadows, and the eventful and realistic portrayal of late Baroque painting. The exact reason for turning towards the Western style is still disputed. However, Greek Catholicism by nature is closer to the Latin Rite, especially in 19th-century Hungary, where most of the population was Latin Catholic. Thus Western art and probably the Catholic rulers of the country, the Habsburgs, influenced the painters and the parish too. (Full article...)
People
- Musicians
Béla Bartók – János Bihari – Ernő Dohnányi – Béni Egressy – Ferenc Erkel – Zoltán Kocsis – Zoltán Kodály – Franz Liszt - Eugene Ormandy - George Szell - András Schiff
- Painters
Gyula Benczúr – Tivadar Csontváry Kosztka – Béla Czóbel – Árpád Feszty – Károly Lotz – Viktor Madarász – Mihály Munkácsy – József Rippl-Rónai – Pál Szinyei Merse – István Szőnyi – Victor Vasarely
- Photographers
Brassaï – Cornell Capa – Robert Capa – Lucien Hervé – André Kertész – László Moholy-Nagy – Martin Munkácsi
- Scientists
Béla H. Bánáthy – Zoltán Bay – Georg von Békésy – Farkas Bolyai – János Bolyai – Károly Bund – József Eötvös – Loránd Eötvös – Dennis Gabor – John Charles Harsanyi – George de Hevesy – Alexander Csoma de Kőrös – László Lovász – John von Neumann – George Andrew Olah – Ernő Rubik – Hans Selye – Ignaz Semmelweis – Charles Simonyi – János Szentágothai – Albert Szent-Györgyi – Leó Szilárd – Edward Teller – Eugene Wigner
- Writers and poets
Endre Ady – János Arany – József Eötvös – György Faludy – Béla Hamvas – Mór Jókai – Attila József – Ferenc Kazinczy – Imre Kertész – János Kodolányi – Ferenc Kölcsey – Imre Madách – Sándor Márai – Ferenc Molnár – Sándor Petőfi – Miklós Radnóti – Magda Szabó – Antal Szerb – Miklós Vámos – Mihály Vörösmarty
- Statesmen, Politicians and Military
Gyula Andrássy – Lajos Batthyány – Gabriel Bethlen – Stephen Bocskay – Matthias Corvinus – Ferenc Deák – Miklós Horthy – Lajos Kossuth – Ferenc Nagy – Imre Nagy – Bertalan Szemere – István Széchenyi – Miklós Wesselényi – Vilmos Nagy of Nagybaczon
- Sportspeople
József Bozsik – Krisztina Egerszegi – Zoltán Gera – Dezső Gyarmati – Ágnes Keleti – Péter Lékó – Csaba Mérő – Tibor Nyilasi – László Papp – Judit Polgár – Zsuzsa Polgár – Ferenc Puskás
- Film & Stage
Nimród Antal – Michael Curtiz – John Garfield – Miklós Jancsó – Sir Alexander Korda – Peter Lorre – Béla Lugosi – Emeric Pressburger – Miklós Rózsa – Andy G. Vajna – Gábor Zsazsa
Samuel Aba (Hungarian: Aba Sámuel; before 990 or c. 1009 – 5 July 1044) reigned as King of Hungary between 1041 and 1044. He was born to a prominent family with extensive domains in the region of the Mátra Hills. Based on reports in the Gesta Hungarorum and other Hungarian chronicles about the non-Hungarian origin of the Aba family, modern historians write that the Abas headed the Kabar tribes that seceded from the Khazar Khaganate and joined the Hungarians in the 9th century.
Around 1009, Samuel or his father married a sister of Stephen I, the first King of Hungary. Thereafter the originally pagan or Judaism (because of Khazar-elite-link) Aba family converted to Christianity. King Stephen appointed Samuel to head the royal court as his palatine. However, the king died in 1038, and the new monarch, Peter the Venetian, removed Samuel from his post. (Full article...)
Selected picture
Wikiprojects
Related projects:
Related portals
Things you can do
| The following stub articles would benefit from expansion. | |
General images -
The following are images from various Hungary-related articles on Wikipedia.
Topics
Categories
New articles
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2025-01-26 21:09 (UTC)
Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
- ICE.T.21 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Imrenehalastyak8 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 20
- Zsuzsa Selyem (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Scope creep (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 50
- Kristian Uldbjerg Hansen (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (160)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 20
- Kontinental '25 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rickyurs (talk · contribs · new pages (39)) started on 2025-01-26, score: 20
- Géza Dávid Turi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jloverdi36 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-25, score: 20
- Gernot Süßmuth (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (66)) started on 2025-01-25, score: 20
- 2024–25 Women's EHF Champions League knockout stage (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kante4 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-25, score: 50
- Gréta Juhász (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fakez76 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-01-25, score: 80
- Lucian Ciocan (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rhinen (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 40
- Károlyi Castle (Carei) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 70
- Károlyi Castle (Szegvár) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 80
- Károlyi Castle (Parádsasvár) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 110
- Mirtill Petrus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fakez76 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 100
- Dávid Jancsó (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MoviesandTelevisionFan (talk · contribs · new pages (33)) started on 2025-01-24, score: 60
- Károlyi Castle (Füzérradvány) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 170
- Ernestine von Fricken (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yadsalohcin (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 20
- Byzantine literature of the Laskaris and Palaiologos periods (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Oliwiasocz (talk · contribs · new pages (27)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 20
- Milan Marjanović (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tomobe03 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 50
- Operation Dugo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Muhandes (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 20
- 2020 Ubisoft sexual misconduct litigation and accusations (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cyberwolf (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 20
- Nataliia Greshchuk (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Silent Kup (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 40
- 2024–25 Austrian Volley League Men (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Killerlicka (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-23, score: 20
- Károlyi Castle (Nagymágocs) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 200
- Nikolett Tóth (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fakez76 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 150
- Bojtor (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rakeck (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 40
- Károlyi Castle (Fehérvárcsurgó) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 140
- Szántai (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rakeck (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 40
- Károlyi Castle (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 50
- Károlyi Castle (Fót) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 70
- René Bernatchez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (66)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 20
- 2016 IIHF U18 Women's World Championship Division I (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Arbitrarily0 (talk · contribs · new pages (60)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 60
- Tamás Papp (handballer) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fakez76 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 90
- Stanisław Michałowski (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rakoon (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-22, score: 20
- József Károlyi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 160
- Ferenc Károlyi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 150
- Naoaki Senaga (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by NST12052002 (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 50
- 1967 Men's World Tennis Circuit (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Navops47 (talk · contribs · new pages (77)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 20
- Agnes of Swabia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Srnec (talk · contribs · new pages (61)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 20
- 2013 3 Hours of Hungaroring (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by KerbHopper (talk · contribs · new pages (19)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 60
- 2023 Fastnet Race (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sinkers009 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-21, score: 20
- The Trip to Panama (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TheDutchArchivist (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 20
- Malcolm Singer (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sfjohna (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-20, score: 40
- Starchess (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 192.54.222.130 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 20
- Vincent (bishop of Várad) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Norden1990 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 70
- Baczko (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Adamtt9 (talk · contribs · new pages (40)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 20
- Zosimus (bishop of Várad) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Norden1990 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 110
- Dorothy Moulton Mayer (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SDGB1217 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2025-01-13, score: 20
- Zosimus, Bishop of Várad (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Norden1990 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 110
- Guido Novak von Arienti (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by PaulTheBoatman10 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 20
- Almásy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 79lives (talk · contribs · new pages (143)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 60
- Marton (name) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Altenmann (talk · contribs · new pages (214)) started on 2025-01-19, score: 40
- Barbara Neumann (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Chaiten1 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2025-01-18, score: 90
- Mate Molnar (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Deligabi (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-18, score: 80
- Because What You Want & What You Get Are Two Completely Different Things Tour (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by FaIsegod (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-18, score: 20
- András Veres (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rutsq (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-18, score: 120
- Three Princesses (Hungarian fairy tale) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by KHR FolkMyth (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-18, score: 80
- Soma Szuhodovszki (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cakesam (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-18, score: 150
- Otto Hieronimus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Anatol Svahilec (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-17, score: 30
- 2024–25 San Francisco Dons women's basketball team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bremerton98310 (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-01-17, score: 30
- List of ambassadors of Austria to Germany (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2025-01-17, score: 20
- 2025 European Short Track Speed Skating Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ruud Buitelaar (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-01-17, score: 20
- Shalva Kiriya (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TheMightyGeneral (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-17, score: 40
- Shapr3D (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cooldudeseven7 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-17, score: 20
- Kurt Sochatzy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MisterBee1966 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-01-17, score: 20
- 2024–25 MŠK Žilina season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CottonTraders (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-17, score: 30
- List of classical music composers by era (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Canstudent (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-17, score: 20
- Sadagat Huseynova (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Qraf (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-16, score: 20
- Anna Řeháková (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SDGB1217 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2025-01-16, score: 20
- Eliška Řeháková (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SDGB1217 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2025-01-16, score: 20
- Miroslav Borshosh (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cilidus (talk · contribs · new pages (100)) started on 2025-01-16, score: 80
- Disappearance of Eliza and Henrietta Huszti (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RWC 01 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-15, score: 30
- List of accolades received by Anora (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Daerl (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-15, score: 20
- Lily Pincus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SDGB1217 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2025-01-15, score: 20
- Gulácsi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Duckmather (talk · contribs · new pages (47)) started on 2025-01-15, score: 20
- The Swan (play) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Saratoga Sam (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-14, score: 60
- János Székely (bishop) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Terot (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-01-14, score: 120
- 23rd Visual Effects Society Awards (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Spanneraol (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-14, score: 20
- Byzantine-Hungarian War (1163-1168) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Damariondennis2007 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-14, score: 20
- 2024–25 Sacramento State Hornets women's basketball team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RedSox39 (talk · contribs · new pages (32)) started on 2025-01-14, score: 30
- Cintia Rodríguez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Happily888 (talk · contribs · new pages (76)) started on 2025-01-14, score: 20
- Hatvanpuszta (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ipflo (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-13, score: 80
- Carl Friedrich Hatzfeldt zu Gleichen (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2025-01-13, score: 30
- Alison Bury (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Espresso Addict (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2025-01-13, score: 20
- ArcGIS Urban (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CJJ2501 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-13, score: 20
- Quartet Diminished (band) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kabootaremesi (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-13, score: 20
- Agnes of Hohenstaufen (died 1184) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Srnec (talk · contribs · new pages (61)) started on 2025-01-13, score: 50
- 2008 12 Hours of Hungary (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by KerbHopper (talk · contribs · new pages (19)) started on 2025-01-13, score: 80
- Magdolna Csath (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sophisticatedevening (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2025-01-12, score: 130
- Téglás (surname) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CaptainOlimar42 (talk · contribs · new pages (46)) started on 2025-01-12, score: 70
- Jutta Pallos-Schönauer (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Scratchinghead (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2025-01-12, score: 50
- List of Poland international footballers born outside Poland (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Marcelus (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-01-12, score: 20
- Peter Kempny (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shyamal (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2025-01-12, score: 20
- M5 (Amsterdam Metro) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Neverland14 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-12, score: 20
- Nabeela Abdulla Al Mulla (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DaffodilOcean (talk · contribs · new pages (26)) started on 2025-01-12, score: 40
- Galician campaign (1213—1214) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Polish Piast (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-01-07, score: 20
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus