
Back Prins Eduard-eilande Afrikaans جزر الأمير إدوارد Arabic Prins-Eduard adaları Azerbaijani Прынс-Эдвард Byelorussian Принц Едуард (архипелаг) Bulgarian Inizi ar Priñs Edouarzh Breton Illes del Príncep Eduard Catalan Prince Edward Islands CEB Ostrovy prince Edvarda Czech Prince Edward Islands Danish
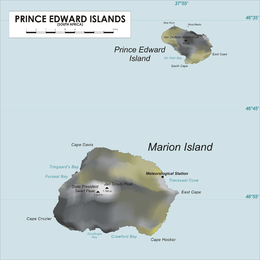 Map of Prince Edward Islands | |
 Orthographic projection centred on the Prince Edward Islands | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Indian Ocean |
| Coordinates | 46°52′48″S 37°45′00″E / 46.88000°S 37.75000°E |
| Area | 343 km2 (132 sq mi)[1] |
| Highest elevation | 1,230 m (4040 ft) |
| Highest point | Mascarin Peak |
| Administration | |
| Province | Western Cape |
| Municipality | City of Cape Town |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 0 (permanent) 50 (non-permanent research staff) |
| Designations | |
|---|---|
| Designated | 24 January 1997 |
| Reference no. | 1688[2] |
The Prince Edward Islands are two small uninhabited subantarctic[3][4][5] volcanic islands in the southern Indian Ocean that are administered by South Africa. They are named Marion Island (named after Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne, 1724–1772) and Prince Edward Island (named after Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn, 1767–1820).
The islands in the group have been declared Special Nature Reserves under the South African Environmental Management: Protected Areas Act, No. 57 of 2003, and activities on the islands are therefore restricted to research and conservation management.[6][7] Further protection was granted when the area was declared a marine protected area in 2013.[8][9] The only human inhabitants of the islands are the staff of a meteorological and biological research station run by the South African National Antarctic Programme on Marion Island.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
USGSwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Prince Edward Islands". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Archived from the original on 28 September 2019. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- ^ Smith, V. R.; Steenkamp, Marianna (November 1990). "Climatic change and its ecological implications at a subantarctic island". Oecologia. 85: 14–24. doi:10.1007/BF00317338.
- ^ Greve, Michelle; Mathakutha, Rabia; Steyn, Christien; Chown, Steven L. (2017). "Terrestrial invasions on sub-Antarctic Marion and Prince Edward Islands". Bothalia - African Biodiversity & Conservation. 47 (2): 1–21. doi:10.4102/abc.v47i2.2143. hdl:2263/66089.
- ^ Crawford, R. J. M.; Cooper, J. (2003). "Conserving Surface-nesting Seabirds at the Prince Edward Islands: The Roles of Research, Monitoring and Legislation". African Journal of Marine Science. 25 (1): 416–425. doi:10.2989/18142320309504031.
- ^ Cooper, John (June 2006). "Antarctica and Islands – Background Research Paper produced for the South Africa Environment Outlook report on behalf of the Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism" (PDF). p. 6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 May 2016. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- ^ 1993 United Nations list of national parks and protected areas. World Conservation Monitoring Centre, International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources, Commission on Natural Parks and Protected Areas, United Nations Environment Programme. 1993. p. 173. ISBN 978-2-8317-0190-5.
- ^ "Prince Edward Islands declared a Marine Protected Area". Department of Environmental Affairs, Republic of South Africa. 9 April 2013. Archived from the original on 12 July 2016.
- ^ "Prince Edward Islands Marine Protected Area: A global treasure setting new conservation benchmarks" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 July 2016.
