
Back فرن تسويط Arabic Pudlovna Czech Pudling Danish Puddelverfahren German Pudelación Spanish Pudeldamine Estonian Putlaus Finnish Puddlage French Suaitheadh (iarann) Irish Kavaró acélgyártás Hungarian
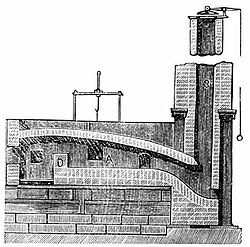
Puddling is the process of converting pig iron to bar (wrought) iron in a coal fired reverberatory furnace. It was developed in England during the 1780s. The molten pig iron was stirred in a reverberatory furnace, in an oxidizing environment to burn the carbon, resulting in wrought iron.[1] It was one of the most important processes for making the first appreciable volumes of valuable and useful bar iron (malleable wrought iron) without the use of charcoal. Eventually, the furnace would be used to make small quantities of specialty steels.
Though it was not the first process to produce bar iron without charcoal, puddling was by far the most successful, and replaced the earlier potting and stamping processes, as well as the much older charcoal finery and bloomery processes. This enabled a great expansion of iron production to take place in Great Britain, and shortly afterwards, in North America. That expansion constitutes the beginnings of the Industrial Revolution so far as the iron industry is concerned. Most 19th century applications of wrought iron, including the Eiffel Tower, bridges, and the original framework of the Statue of Liberty, used puddled iron.
- ^ "Smelting Science - 1. Furnaces". www.tf.uni-kiel.de. Faculty of Engineering-Kiel University. Archived from the original on May 22, 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2024.