
Back كيمو (برنامج محاكاة) Arabic QEMU Catalan QEMU Czech QEMU German QEMU Spanish کیوییامیو Persian QEMU Finnish QEMU French QEMU Croatian QEMU ID
This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. (December 2024) |
 | |
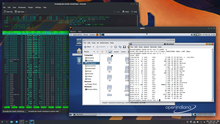 The free operating system OpenIndiana running within QEMU, which runs as a process on Linux | |
| Original author(s) | Fabrice Bellard |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | QEMU team: Peter Maydell, et al. |
| Stable release | 9.2.2[1] |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Linux, Microsoft Windows, macOS and some other UNIX platforms |
| Type | Hypervisor, Emulator |
| License | GPL-2.0-only[2] |
| Website | www |
The Quick Emulator (QEMU)[3] is a free and open-source emulator that uses dynamic binary translation to emulate a computer's processor; that is, it translates the emulated binary codes to an equivalent binary format which is executed by the machine. It provides a variety of hardware and device models for the virtual machine, enabling it to run different guest operating systems. QEMU can be used with a Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) to emulate hardware at near-native speeds. Additionally, it supports user-level processes, allowing applications compiled for one processor architecture to run on another.[4]
QEMU supports the emulation of x86, ARM, PowerPC, RISC-V, and other architectures.
- ^ "[ANNOUNCE] QEMU 9.2.2 Stable released". 25 February 2025. Retrieved 25 February 2025.
- ^ "License - QEMU".
- ^ "Glossary". National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 2023-04-24.
- ^ Speed, Richard (2019-04-25). "QEMU 4 arrives with toys for Arm admirers, RISC-V revolutionaries, POWER patriots... you get the idea". www.theregister.co.uk. The Register. Archived from the original on 2019-10-01. Retrieved 2019-10-01.