
Back Quasi-Zenith Satellite System Catalan Quasi-Zenith Satellite System Czech Quasi-Zenit-Satelliten-System German Quasi-Zenith Spanish سامانه ماهوارهای کواسی-زنیث Persian QZSS Finnish Quasi-Zenith Satellite System French QZSS HE Sistem Satelit Quasi-Zenith ID Sistema satellitare Quasi-Zenith Italian
 | |
| Country/ies of origin | Japan |
|---|---|
| Operator(s) | Quasi-Zenith Satellite System Services Inc. / Cabinet Office |
| Type | Civilian |
| Status | Operational |
| Coverage | Regional |
| Accuracy | PNT <10 m (public) SLAS <1 m (public) CLAS <10 cm (public) |
| Constellation size | |
| Nominal satellites | 7 |
| Current usable satellites | 4 |
| First launch | 11 September 2010 |
| Last launch | 26 October 2021 |
| Total launches | 5 |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Regime(s) | 3x GSO |
| Other details | |
| Cost | JPY 170 billion |
| Website | qzss |
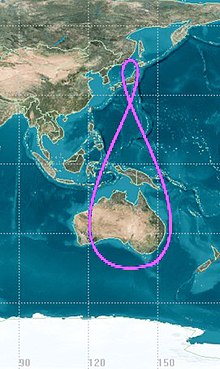
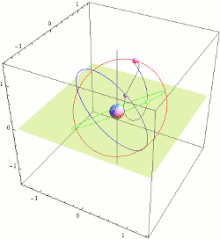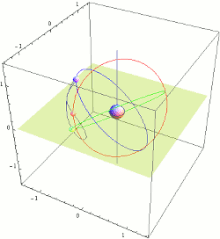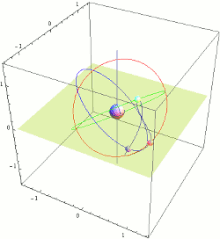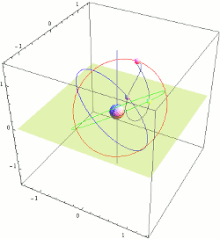
The Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), also known as Michibiki (みちびき, "guidance"), is a four-satellite regional satellite navigation system and a satellite-based augmentation system developed by the Japanese government to enhance the United States-operated Global Positioning System (GPS) in the Asia-Oceania regions, with a focus on Japan.[1] The goal of QZSS is to provide highly precise and stable positioning services in the Asia-Oceania region, compatible with GPS.[2] Four-satellite QZSS services were available on a trial basis as of 12 January 2018,[3] and officially started on 1 November 2018.[4] A satellite navigation system independent of GPS is planned for 2023 with seven satellites.[5][6] In May 2023 it was announced that the system would expand to eleven satellites.[7]
- ^ "Quasi-Zenith Satellite Orbit (QZO)". Archived from the original on 9 March 2018. Retrieved 10 March 2018.
- ^ "[Movie] Quasi-Zenith Satellite System "QZSS"". Quasi-Zenith Satellite System(QZSS). Archived from the original on 15 July 2017. Retrieved 19 July 2017.
- ^ "Start of QZS-4 Trial Service". Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS). Archived from the original on 10 August 2018. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- ^ "Japan's QZSS service now officially available". 26 November 2018. Retrieved 11 January 2019.
- ^ "Japan mulls seven-satellite QZSS system as a GPS backup". SpaceNews. 15 May 2017. Retrieved 10 August 2019.
- ^ Kriening, Torsten (23 January 2019). "Japan Prepares for GPS Failure with Quasi-Zenith Satellites". SpaceWatch.Global. Retrieved 10 August 2019.
- ^ Kawahara, Satoshi (8 May 2023). "Japan plans expansion of homegrown GPS network to 11 satellites". Nikkei Asia.