Back RV الثور Arabic RV Tauri AST RV del Taure Catalan RV Tauri German RV Tauri Spanish آروی گاو Persian RV Tauri French RV Tauri Italian おうし座RV星 Japanese RV Тельца Russian
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Taurus |
| Right ascension | 04h 47m 6.7281s[2] |
| Declination | 26° 10′ 45.613″[2] |
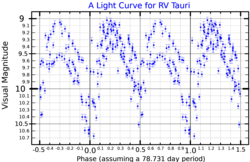
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 9.0–10.6[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Post-AGB[4] |
| Spectral type | G2eIa-M2Ia[5] |
| U−B color index | 0.9-1.8[3] |
| B−V color index | 1.5-1.9[3] |
| Variable type | RVb[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 32[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 1.557[7] mas/yr Dec.: −4.717[7] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.6926 ± 0.0605 mas[7] |
| Distance | 4,700 ± 400 ly (1,400 ± 100 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −3.359[8] |
| Orbit[4] | |
| Period (P) | 1,198±17 d |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 1.5 AU |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.5±0.1 |
| Inclination (i) | 71±8° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 14.5±1.6 km/s |
| Details | |
| A | |
| Mass | 0.53[4] M☉ |
| Radius | 83.4±12.8[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 2,800[4] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.6[4] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,810±200[4] (4,225-5,080[3]) K |
| Metallicity | −0.3±0.2[4] |
| B | |
| Mass | 0.7±0.1[4] M☉ |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
RV Tauri (RV Tau) is a star in the constellation Taurus. It is a yellow supergiant and is the prototype of a class of pulsating variables known as RV Tauri variables. It is a post-AGB star and a spectroscopic binary about 4,700 light years away.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
ASASServerwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Hog, E.; Kuzmin, A.; Bastian, U.; Fabricius, C.; Kuimov, K.; Lindegren, L.; Makarov, V. V.; Roeser, S. (1998). "The TYCHO Reference Catalogue". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 335: L65. Bibcode:1998A&A...335L..65H.
- ^ a b c d Dawson, D. W. (1979). "A photometric investigation of RV Tauri and yellow semiregular variables". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 41: 97. Bibcode:1979ApJS...41...97D. doi:10.1086/190610.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Manick, Rajeev; Kamath, Devika; Van Winckel, Hans; Jorissen, Alain; Sekaran, Sanjay; Bowman, Dominic M.; Oomen, Glenn-Michael; Kluska, Jacques; Bollen, Dylan; Waelkens, Christoffel (2019). "Spectroscopic binaries RV Tauri and DF Cygni". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 628: A40. arXiv:1906.10492. Bibcode:2019A&A...628A..40M. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201834956. S2CID 195584310.
- ^ Taranova, O. G.; Shenavrin, V. I.; Tatarnikov, A. M. (2009). "Infrared photometry for two RV Tau stars and V1027 Cyg". Astronomy Letters. 35 (7): 472. Bibcode:2009AstL...35..472T. doi:10.1134/S1063773709070044. S2CID 120327422.
- ^ Wilson, Ralph Elmer (1953). "General catalogue of stellar radial velocities". Washington: 0. Bibcode:1953GCRV..C......0W.
- ^ a b c Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ a b Bódi, A.; Kiss, L. L. (2019). "Physical properties of galactic RV Tauri stars from Gaia DR2 data". The Astrophysical Journal. 872 (1): 60. arXiv:1901.01409. Bibcode:2019ApJ...872...60B. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aafc24. S2CID 119099605.