
Back Republica de Bosnia y Herzegovina AN جمهورية البوسنة والهرسك Arabic Bosniya və Herseqovina Respublikası Azerbaijani بوسنی و هرزقوین جومهوریتی AZB Босния һәм Герцеговина Республикаһы Bashkir Рэспубліка Боснія і Герцагавіна Byelorussian Рэспубліка Босьнія і Герцагавіна BE-X-OLD Република Босна и Херцеговина (1992 – 1997) Bulgarian Republika Bosna i Hercegovina BS República de Bòsnia i Hercegovina Catalan
Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina Republika Bosna i Hercegovina Република Босна и Херцеговина | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992–1995 | |||||||||||
| Anthem: Једна си једина Jedna si jedina "You are the one and only" | |||||||||||
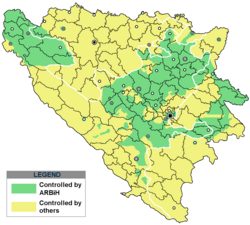 All territory once fully controlled and administered by the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina during the Bosnian War[when?] Territory internationally recognised as part of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, but controlled by other entities during the Bosnian War[citation needed] | |||||||||||
| Capital | Sarajevo | ||||||||||
| Official languages | Serbo-Croatian[1] | ||||||||||
| Religion | Islam Christianity | ||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Bosnian | ||||||||||
| Government | Unitary dominant-party parliamentary republic | ||||||||||
| Chairman of the Presidency | |||||||||||
• 1992–1996 | Alija Izetbegović | ||||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||||
• 1992 | Jure Pelivan | ||||||||||
• 1992–1993 | Mile Akmadžić | ||||||||||
• 1993–1996 | Haris Silajdžić | ||||||||||
• 1996–1997 | Hasan Muratović | ||||||||||
| Legislature | National Assembly | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Breakup of Yugoslavia | ||||||||||
| 1 March 1992 | |||||||||||
| 3 March 1992 | |||||||||||
| 6 April 1992 | |||||||||||
| 18 October 1992 | |||||||||||
| 18 March 1994 | |||||||||||
| 14 December 1995 | |||||||||||
| Currency | BH Dinar | ||||||||||
| Calling code | +387 | ||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | BA | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Serbo-Croatian: Republika Bosna i Hercegovina / Република Босна и Херцеговина) was a state in Southeastern Europe, existing from 1992 to 1995. It is the direct legal predecessor to the modern-day state of Bosnia and Herzegovina.[2]
Bosnia and Herzegovina seceded from the disintegrating Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia on 3 March 1992. The Bosnian War broke out soon after its Declaration of Independence and lasted for 3 years. Leaders from two of the three main ethnicities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, namely the Serbs and the Croats, separately established the entities of the Republika Srpska and the Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, respectively, which were unrecognized by the Bosnian state and international governments.[3] Informally, these events were considered as evidence that the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina represented primarily its Bosniak (mainly Muslim) population, though formally, the presidency and government of the republic was still composed of Serbs and Croats along with Bosniaks.[4][5][6]
Under the Washington Agreement of 1994, however, Bosniaks were joined by Herzeg-Bosnia, in support for the Republic by the formation of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, a sub-state joint entity. In 1995, the Dayton Peace Accords joined the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina with the Serb entity, Republika Srpska, from that point onward recognized formally as a political sub-state entity without a right of secession, into the state of Bosnia and Herzegovina.[3][5][7]
The prefix Republic was removed following the co-signing of the Annex 4 of the Dayton Agreement, containing the constitution of Bosnia and Herzegovina, on 14 December 1995.
- ^ "Ustav RBiH.pdf" (PDF). Fondacija Centar za javno pravo. 14 March 1993. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
U Republici Bosni i Hercegovini u službenoj upotrebi je srpskohrvatski odnosno hrvatskosrpski jezik ijekavskog izgovora.
- ^ "CONSTITUTION OF BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA" (PDF). The Constitutional Court of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 June 2013.
- ^ a b Holbrooke, Richard C. (1999). To End a War. Modern Library. ISBN 9780375753602.
- ^ Hoare, Marko Attila (2004). How Bosnia armed. Saqi Books in association with the Bosnian Institute. ISBN 9780863563676.
- ^ a b Simms, Brendan (4 July 2002). Unfinest Hour: Britain and the Destruction of Bosnia. Penguin Books Limited. ISBN 9780140289831.
- ^ Bose, Sumantra (2002). Bosnia After Dayton: Nationalist Partition and International Intervention. C. Hurst. ISBN 9781850656456.
- ^ Vranić, Jelena (2000). The Dayton peace accords: mapping negotiations : based on "To end a war" book by Richard Holbrooke. Fama. ISBN 9789958954917. Retrieved 7 September 2016.

