| Retropharyngeal space | |
|---|---|
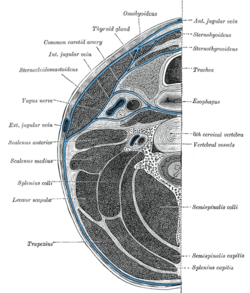 Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. Showing the arrangement of the deep cervical fascia | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | spatium retropharyngeum |
| TA98 | A05.3.01.118 |
| TA2 | 2884 |
| FMA | 84965 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The retropharyngeal space (abbreviated as "RPS"[1][2]) is a potential space[2][3] and deep compartment of the head and neck[1] situated posterior to the pharynx.[4] The RPS is bounded anteriorly by the buccopharyngeal fascia, posteriorly by the alar fascia, and laterally by the carotid sheath. It extends between the base of the skull superiorly, and the mediastinum inferiorly.[1] It contains the retropharyngeal lymph nodes.[2] Its function is to facilitate movements in the superoinferior axis of the larynx, pharynx, and esophagus in relation to the cervical spine.[3]
Sources consider the retropharyngeal space to be in principle subdivided into the so-called "true retropharyngeal space"[1][5] or "retropharyngeal space proper" (part of the RPS situated anterior to the alar fascia),[5][2] and the danger space (part of the RPS situated posterior to the alar fascia).[1][2][5] The danger space is sometimes also lumped together with the true RPS and the whole referred to as the RPS because the alar fascia is an ineffective barrier.[2] Infections from the head and neck can spread down through the danger space into the posterior mediastinum.[2]
- ^ a b c d e Mnatsakanian A, Minutello K, Bordoni B (2022). "Anatomy, Head and Neck, Retropharyngeal Space". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 30725729. Retrieved 2022-07-24.
- ^ a b c d e f g Chong VF, Fan YF (October 2000). "Radiology of the Retropharyngeal Space". Clinical Radiology. 55 (10): 740–748. doi:10.1053/crad.2000.0510. PMID 11052873.
- ^ a b Morton, David A. (2019). The Big Picture: Gross Anatomy. K. Bo Foreman, Kurt H. Albertine (2nd ed.). New York. p. 266. ISBN 978-1-259-86264-9. OCLC 1044772257.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ "Spatium retropharyngeum". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 2022-07-24.
- ^ a b c Debnam JM, Guha-Thakurta N (December 2012). "Retropharyngeal and prevertebral spaces: anatomic imaging and diagnosis". Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America. 45 (6): 1293–1310. doi:10.1016/j.otc.2012.08.004. PMC 3994542. PMID 23153750.
