
Back موشور معيني Arabic Romboedre Catalan Klenec Czech Ромбоэдр CV Romboeder Danish Rhomboeder German Romboedro Esperanto Romboedro Spanish Erronboedro Basque لوزوجه Persian
| Rhombohedron | |
|---|---|
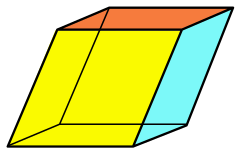
| |
| Type | prism |
| Faces | 6 rhombi |
| Edges | 12 |
| Vertices | 8 |
| Symmetry group | Ci , [2+,2+], (×), order 2 |
| Properties | convex, equilateral, zonohedron, parallelohedron |
In geometry, a rhombohedron (also called a rhombic hexahedron[1][2] or, inaccurately, a rhomboid[a]) is a special case of a parallelepiped in which all six faces are congruent rhombi.[3] It can be used to define the rhombohedral lattice system, a honeycomb with rhombohedral cells. A rhombohedron has two opposite apices at which all face angles are equal; a prolate rhombohedron has this common angle acute, and an oblate rhombohedron has an obtuse angle at these vertices. A cube is a special case of a rhombohedron with all sides square.
- ^ Miller, William A. (January 1989). "Maths Resource: Rhombic Dodecahedra Puzzles". Mathematics in School. 18 (1): 18–24. JSTOR 30214564.
- ^ Inchbald, Guy (July 1997). "The Archimedean honeycomb duals". The Mathematical Gazette. 81 (491): 213–219. doi:10.2307/3619198. JSTOR 3619198.
- ^ Coxeter, HSM. Regular Polytopes. Third Edition. Dover. p.26.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).