
Back Rio Grande Afrikaans ريو غراندي Arabic نهر ريو جراندى ARZ Ríu Bravo AST ریو قرانده چایی AZB Рио-Гранде (Мексика ҡултығына ҡойоусы йылға) Bashkir Рыа-Грандэ Byelorussian Рио Гранде Bulgarian रियो ग्रांडे Bihari রিও গ্রান্দে Bengali/Bangla
| Rio Grande Río Bravo del Norte (in Spanish), Tooh Baʼáadii (in Navajo), Kótsoi (in Jicarilla Apache) | |
|---|---|
 The Rio Grande at Big Bend National Park, on the Mexico–U.S. border | |
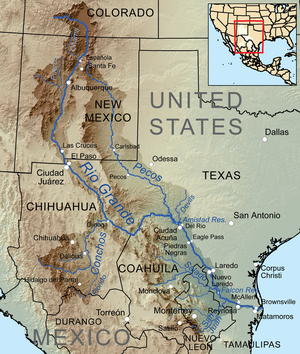 Map of the Rio Grande drainage basin | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States, Mexico |
| State | Colorado, New Mexico, Texas, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, Tamaulipas |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Main stem source: Canby Mountain, Continental Divide |
| • location | San Juan Mountains, Rio Grande National Forest,[1] Colorado, United States |
| • coordinates | 37°47′51″N 107°32′35″W / 37.79750°N 107.54306°W[3] |
| • elevation | 12,000 ft (3,700 m)[1] |
| 2nd source | Most distant source: Pole creek, Tundra Top peak 13450, Continental Divide[4] |
| • location | San Juan Mountains, Rio Grande National Forest,[1] Colorado, United States |
| • coordinates | 37°51′6″N 107°25′28″W / 37.85167°N 107.42444°W |
| • elevation | 12,760 ft (3,890 m) |
| Mouth | Gulf of Mexico |
• location | Cameron County, Texas; Matamoros, Tamaulipas |
• coordinates | 25°57′22″N 97°8′43″W / 25.95611°N 97.14528°W[3] |
• elevation | 0 ft (0 m) |
| Length | 1,896 mi (3,051 km)[1] |
| Basin size | 182,200 sq mi (472,000 km2)[5] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Eagle Pass, Texas – Piedras Negras, Coahuila[2] |
| • average | 2,403 cu ft/s (68.0 m3/s)[2] |
| • minimum | 24 cu ft/s (0.68 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 964,000 cu ft/s (27,300 m3/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Red River, Rio Hondo, Rio Pueblo de Taos, Embudo Creek, Santa Fe River, Galisteo Creek, Alamito Creek, Terlingua Creek, Pecos River, Devils River |
| • right | Conejos River, Rio Chama, Jemez River, Rio Puerco, Rio Conchos, Rio Salado, Rio Alamo, San Juan River |
| Type | Wild 150.1 miles (241.6 km) Scenic 108.5 miles (174.6 km) Recreational 0.8 miles (1.3 km) |
| Designated | October 2, 1968[6] |
The Rio Grande (/ˌriːoʊ ˈɡrænd/ or /ˌriːoʊ ˈɡrɑːndeɪ/) in the United States or the Río Bravo (del Norte) in Mexico (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈri.o ˈβɾaβo ðel ˈnoɾte]), also known as P’osoge in Tewa and Tó Ba’áadi in Navajo,[7] is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the Southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.[8][9][10] The length of the Rio Grande is 1,896 miles (3,051 km), making it the 4th longest river in the United States and in North America by main stem. It originates in south-central Colorado, in the United States, and flows to the Gulf of Mexico.[11] The Rio Grande drainage basin (watershed) has an area of 182,200 square miles (472,000 km2);[5] however, the endorheic basins that are adjacent to and within the greater drainage basin of the Rio Grande increase the total drainage-basin area to 336,000 square miles (870,000 km2).[12]
The Rio Grande with its fertile valley, along with its tributaries, is a vital water source for seven US and Mexican states, and flows primarily through arid and semi-arid lands. After traversing the length of New Mexico, the Rio Grande becomes the Mexico–United States border, between the U.S. state of Texas and the northern Mexican states of Chihuahua and Coahuila, Nuevo León and Tamaulipas; a short segment of the Rio Grande is a partial state-boundary between the U.S. states of New Mexico and Texas. Since the mid–twentieth century, only 20 percent of the Rio Grande's water reaches the Gulf of Mexico, because of the voluminous consumption of water required to irrigate farmland (e.g. the Mesilla and Lower Rio Grande Valleys) and to continually hydrate cities (e.g. Albuquerque); such water usages are additional to the reservoirs of water retained with diversion dams.[1] 260 miles (418 km) of the river in New Mexico and Texas are designated as the Rio Grande Wild and Scenic River.[13]
- ^ a b c d e Metz, Leon C. "Rio Grande". The Handbook of Texas Online. Retrieved July 17, 2010.
- ^ a b "Water Bulletin Number 75: Flow of the Rio Grande and Related Data; From Elephant Butte Dam, New Mexico to the Gulf of Mexico". International Boundary and Water Commission. 2005. Retrieved July 17, 2010.
- ^ a b "Rio Grande". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior.
- ^ Tundra Top
- ^ a b "Rio Grande NASQAN Program". United States Geological Survey. Archived from the original on July 4, 2011. Retrieved July 17, 2010.
- ^ "National Wild and Scenic Rivers System". National Wild and Scenic Rivers System. Retrieved January 5, 2023.
- ^ Monforti, Jessica Lavariega; Graham, Margaret A. "The Rio Grande". obo. Retrieved June 5, 2024.
- ^ Oxford Pronunciation June 28, 2017
- ^ "Rio Grande". Encyclopedia of Santa Fe. Archived from the original on May 8, 2021. Retrieved June 28, 2017.
- ^ Brians, Paul (May 26, 2016). "rio grande river / rio grande". Paul Brians. Retrieved June 28, 2017 – via Washington State University.
- ^ "Mighty Rio Grande Now a Trickle Under Siege". The New York Times. April 13, 2015.
- ^ Benke, Arthur C.; Cushing, Colbert E. (2005). Rivers of North America. Academic Press. pp. 186–192. ISBN 978-0120882533.
- ^ "Rio Grande Wild & Scenic River". Bureau of Land Management.