
Back ريو غراندي دي مينداناو Arabic ریو قرانده ده میندانائو چایی AZB Минданао (река) Bulgarian Mindanao River (suba sa Pilipinas) CEB Pulangi Czech Rio Grande de Mindanao German Río Grande de Mindanao Spanish Rio Grande de Mindanao French Karayan Mindanao ILO Rio Grande de Mindanao Italian
Rio Grande de Mindanao
| |
|---|---|
 | |
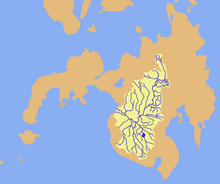 Drainage map of Mindanao River | |
Mindanao River mouth | |
| Location | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | |
| Province | |
| Cities | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Kitanglad Mountain Range |
| • location | Brgy. Kalabugao, Impasugong, Bukidnon |
| • coordinates | 8°27′15″N 125°09′46″E / 8.45417°N 125.16278°E |
| Mouth | Illana Bay |
• location | Cotabato City |
• coordinates | 7°15′20″N 124°12′0″E / 7.25556°N 124.20000°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 373 km (232 mi)[1] |
| Basin size | 23,169 km2 (8,946 sq mi)[2] |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 1,400 m3/s (49,000 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 3,000 m3/s (110,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | |
| • right | |
The Rio Grande de Mindanao, also known as the Mindanao River, is the second-largest river system in the Philippines. Located on the southern island of Mindanao, with a total drainage area of 23,169 km2 (8,946 sq mi),[2] draining the majority of the central and eastern portion of the island, and a total length of approximately 373 km (232 mi).[1][3] It is an important transportation artery, used mainly in transporting agricultural products and, formerly, timber.
Its headwaters are in the mountains of Impasugong, Bukidnon, south of Gingoog in Misamis Oriental, where it is called the Pulangi River. Joining the Kabacan River, it becomes the Mindanao River. Flowing out of the mountains, it forms the center of a broad, fertile plain in the southcentral portion of the island. Before its mouth in Illana Bay, it splits into two parallel sections, the Cotabato and Tamontaka, separated by a 180 m (590 ft) hill.
Population centers along the river include Cotabato City, Datu Piang and Midsayap.
- ^ a b Kenneth Kimutai too (July 24, 2018). "Longest Rivers In The Philippines". worldatlas.com. WorldAtlas. Retrieved September 6, 2019.
- ^ a b Vicente B. Tuddao Jr. (September 21, 2011). "Water Quality Management in the Context of Basin Management: Water Quality, River Basin Management and Governance Dynamics in the Philippines" (PDF). www.wepa-db.net. Department of Environment and Natural Resources. Retrieved April 5, 2017.
- ^ Principal River Basins of the Philippines, published by the National Water Resources Board, October 1976 (p. 12)

