
Back Арумын бызшәа Abkhazian Roemeens Afrikaans Rumänische Sprache ALS ሩማንኛ Amharic Idioma rumano AN Rumǣnisc sprǣc ANG रोमानियाई भाषा ANP اللغة الرومانية Arabic ܠܫܢܐ ܪܘܡܢܝܐ ARC الرومانية ARY
| Romanian | |
|---|---|
| Daco-Romanian | |
| limba română, românește, română[a] | |
| Pronunciation | [roˈmɨnə] |
| Native to | Romania, Moldova |
| Region | Central Europe, Southeastern Europe, and Eastern Europe |
| Ethnicity | |
Native speakers | 25 million (2020)[1] |
Early forms | |
| Dialects | |
| |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Romanian Academy |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | ro |
| ISO 639-2 | rum (B) ron (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | ron |
| Glottolog | roma1327 |
| Linguasphere | (varieties: 51-AAD-ca to -ck) 51-AAD-c (varieties: 51-AAD-ca to -ck) |
 Blue: region where Romanian is the dominant language. Cyan: areas with a notable minority of Romanian speakers. | |
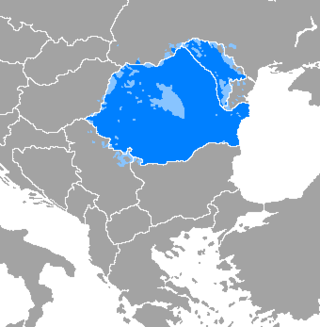 Distribution of the Romanian language in Romania, Moldova and surroundings | |
Romanian (obsolete spelling: Roumanian; endonym: limba română [ˈlimba roˈmɨnə] ⓘ, or românește [romɨˈneʃte], lit. 'in Romanian') is the official and main language of Romania and Moldova. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin which separated from the Western Romance languages in the course of the period from the 5th to the 8th centuries.[12] To distinguish it within the Eastern Romance languages, in comparative linguistics it is called Daco-Romanian as opposed to its closest relatives, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian. It is also spoken as a minority language by stable communities in the countries surrounding Romania (Bulgaria, Hungary, Serbia and Ukraine), and by the large Romanian diaspora. In total, it is spoken by 25 million people as a first language.[1]
Romanian was also known as Moldovan in Moldova, although the Constitutional Court of Moldova ruled in 2013 that "the official language of Moldova is Romanian".[c] On 16 March 2023, the Moldovan Parliament approved a law on referring to the national language as Romanian in all legislative texts and the constitution. On 22 March, the president of Moldova, Maia Sandu, promulgated the law.[13]
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ a b Romanian at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)

- ^ Petrucci 1999, p. 4.
- ^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian (10 July 2023). "Glottolog 4.8 - Eastern Romance". Glottolog. Leipzig: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. doi:10.5281/zenodo.7398962. Archived from the original on 21 November 2023. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ "ARTICOLUL 13 – Constitutia României". Cdep.ro. Archived from the original on 7 September 2011. Retrieved 28 January 2016.
- ^ "Modificat și în Constituție: "Limba de stat a Republicii Moldova este limba română" – FOTO" (in Romanian). ProTV Chișinău. 30 March 2023. Archived from the original on 31 March 2023. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ^ Untila, Stela (14 July 2021). ""Cât există Transnistria, va exista "limba moldovenească". Krasnoselski, despre posibile divergențe cu Chișinăul". NewsMaker (in Romanian). Archived from the original on 2 April 2023. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ^ "Official use of languages and scripts in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina". Provincial Secretariat for Regulations, Administration and National Minorities. Archived from the original on 25 October 2020. Retrieved 18 October 2010.
- ^ "The Commission's use of languages". Archived from the original on 3 April 2023. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ^ "Hungary needs to strengthen use of and access to minority languages". Council of Europe. Archived from the original on 27 August 2019. Retrieved 16 January 2019.
- ^ "Latest Council of Europe report on regional or minority Languages in Serbia published". The Network to Promote Linguistic Diversity. Archived from the original on 26 June 2015. Retrieved 25 June 2015.
- ^ Gherman, Marin (13 March 2023). "Cum îi ajută pe românii din Ucraina înlocuirea limbii "moldovenești" cu limba română". Libertatea (in Romanian). Archived from the original on 2 April 2023. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ^ "Istoria limbii române" ("History of the Romanian Language"), II, Academia Română, Bucharest, 1969
- ^ "Președinta Maia Sandu a promulgat Legea care confirmă că limba de stat a Republicii Moldova este cea română" (in Romanian). Presidency of the Republic of Moldova.
Astăzi am promulgat Legea care confirmă un adevăr istoric și incontestabil: limba de stat a Republicii Moldova este cea română.
[Today I have promulgated the law that confirms a historical and indisputable truth: the state language of the Republic of Moldova is Romanian.][permanent dead link]