
Back Rootsovo dmychadlo Czech Roots-kompressor Danish Roots-Gebläse German Compresor volumétrico tipo Roots Spanish Compresseur Roots French Roots (pompa da vuoto) Italian スーパーチャージャー#ルーツ式 Japanese Rootscompressor Dutch Sprężarka z wirującymi tłokami Polish Rootsovo dúchadlo Slovak
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2014) |
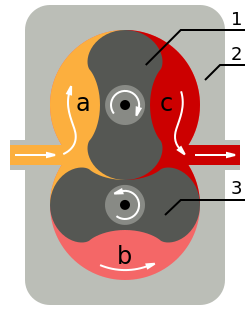
- Rotary vane 1
- Pump body
- Rotary vane 2
- Intake
- Pumping
- Output
The Roots blower is a positive displacement lobe pump which operates by pumping a fluid with a pair of meshing lobes resembling a set of stretched gears. Fluid is trapped in pockets surrounding the lobes and carried from the intake side to the exhaust.
The Roots blower design does not incorporate any reduction in volume/increase in pressure as air or other fluid passes through, hence it can best be described as a blower rather than a supercharger unlike some other designs of "supercharger" such as cozette, centric, Shorrock supercharger, Powerplus supercharger and also the axial flow Eaton type supercharger which have internal "compression".
The most common application of the Roots-type blower has been the induction device on two-stroke diesel engines, such as those produced by Detroit Diesel and Electro-Motive Diesel. Roots-type blowers are also used to supercharge four-stroke Otto cycle engines, with the blower being driven from the engine's crankshaft via a toothed or V-belt, a roller chain or a gear train.
The Roots-type blower is named after American inventors and brothers Philander and Francis Marion Roots, founders of the Roots Blower Company of Connersville, Indiana, who patented the basic design in 1860 as an air pump for use in blast furnaces and other industrial applications. In 1900, Gottlieb Daimler included a Roots-style blower in a patented engine design, making the Roots-type blower the oldest of the various designs now available. Roots blowers are commonly referred to as air blowers or PD (positive displacement) blowers.[1]
- ^ http://www.airblowerservices.com , Air Blower Services