
Back Russiese inval in Oekraïne sedert 2022 Afrikaans ዘረኝነት በሩሶ-ዩክሬንያን ጦርነት Amharic Invasión rusa d'Ucraína de 2022 AN 2022 infaru Russlandes on Ucrægnan ANG الغزو الروسي لأوكرانيا Arabic جتياح روسي د ؤكرانيا د 2022 ARY الغزو الروسى لاوكرانيا (2022) ARZ ইউক্ৰেইনৰ ওপৰত ৰাছিয়াৰ আক্ৰমণ Assamese Invasión rusa d'Ucraína de 2022 AST Rusiya–Ukrayna müharibəsi (2022–hal-hazırda) Azerbaijani
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| Russian invasion of Ukraine | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Russo-Ukrainian War (outline) | |||||||
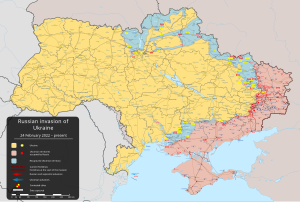 Map of Ukraine as of 6 January 2025[update] (details): Continuously controlled by Ukraine
| |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
Supported by: |
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
| Order of battle | Order of battle | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
Pre-invasion at border: 169,000–190,000[e][5][6][7] Pre-invasion total: 900,000 military[8] 554,000 paramilitary[8] In February 2023: 300,000+ active personnel in Ukraine[9] In June 2024: 700,000 active personnel in the area[10] |
Pre-invasion total: 196,600 military[11] 102,000 paramilitary[11] July 2022 total: up to 700,000[12] September 2023 total: over 800,000[13] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Reports vary widely, see § Casualties for details. | |||||||
|
| |||||||
On 24 February 2022, Russia invaded Ukraine in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which started in 2014. The invasion, the largest and deadliest conflict in Europe since World War II,[14][15][16] has caused hundreds of thousands of military casualties and tens of thousands of Ukrainian civilian casualties. As of 2024, Russian troops occupy about 20% of Ukraine. From a population of 41 million, about 8 million Ukrainians had been internally displaced and more than 8.2 million had fled the country by April 2023, creating Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II.
In late 2021, Russia massed troops near Ukraine's borders and issued demands to the West including a ban on Ukraine ever joining the NATO military alliance.[17] After repeatedly denying having plans to attack Ukraine, on 24 February 2022, Russian president Vladimir Putin announced a "special military operation", saying that it was to support the Russian-backed breakaway republics of Donetsk and Luhansk, whose paramilitary forces had been fighting Ukraine in the Donbas conflict since 2014. Putin espoused irredentist and imperialist views challenging Ukraine's legitimacy as a state, baselessly claimed that the Ukrainian government were neo-Nazis committing genocide against the Russian minority in the Donbas, and said that Russia's goal was to "demilitarise and denazify" Ukraine.[18][19][20][21] Russian air strikes and a ground invasion were launched on a northern front from Belarus towards the capital Kyiv, a southern front from Crimea, and an eastern front from the Donbas and towards Kharkiv. Ukraine enacted martial law, ordered a general mobilisation and severed diplomatic relations with Russia.
Russian troops retreated from the north and the outskirts of Kyiv by April 2022, after encountering stiff resistance and logistical challenges. The Bucha massacre was uncovered after their withdrawal. In the southeast, Russia launched an offensive in the Donbas and captured Mariupol after a destructive siege. Russia continued to bomb military and civilian targets far from the front, and struck the energy grid through the winter months. In late 2022, Ukraine launched successful counteroffensives in the south and east, liberating most of Kharkiv province. Soon after, Russia illegally annexed four partly-occupied provinces. In November, Ukraine liberated Kherson. In June 2023, Ukraine launched another counteroffensive in the southeast but made few gains. After small but steady Russian advances in the east in the first half of 2024, Ukraine launched a cross-border offensive into Russia's Kursk Oblast in August. The United Nations Human Rights Office reports that Russia is committing severe human rights violations in occupied Ukraine.
The invasion was met with widespread international condemnation. The United Nations General Assembly passed a resolution condemning the invasion and demanding a full Russian withdrawal. The International Court of Justice ordered Russia to halt military operations, and the Council of Europe expelled Russia. Many countries imposed sanctions on Russia and its ally Belarus and provided humanitarian and military aid to Ukraine. The Baltic states and Poland declared Russia a terrorist state. Protests occurred around the world, with anti-war protesters in Russia being met by mass arrests and greater media censorship. The Russian attacks on civilians have led to allegations of genocide.[22][23][24][25] War-related disruption to Ukrainian agriculture and shipping contributed to a world food crisis, while war-related environmental damage has been described as ecocide. The International Criminal Court (ICC) opened an investigation into crimes against humanity, war crimes, abduction of Ukrainian children, and genocide against Ukrainians. The ICC issued arrest warrants for Putin and Maria Lvova-Belova and for four Russian military officials.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Graham-Harrison, Emma and McCurry, Justin (10 October 2024). "North Koreans deployed alongside Russian troops in Ukraine, sources say". The Guardian. Retrieved 10 October 2024.
- ^ Lister, Tim; Kesa, Julia (24 February 2022). "Ukraine says it was attacked through Russian, Belarus and Crimea borders". Kyiv: CNN. Archived from the original on 24 February 2022. Retrieved 24 February 2022.
- ^ Murphy, Palu (24 February 2022). "Troops and military vehicles have entered Ukraine from Belarus". CNN. Archived from the original on 23 February 2022. Retrieved 24 February 2022.
- ^ "Missiles launched into Ukraine from Belarus". BBC News. 27 February 2022. Archived from the original on 2 March 2022. Retrieved 27 February 2022.
- ^ "75 тысяч погибших российских солдат 120 смертей в день – вот цена, которую платит Россия за нападение на соседнюю страну. Новое большое исследование «Медузы» и «Медиазоны» о потерях". Meduza (in Russian). Retrieved 24 February 2024.
... численность войск на фронте (если при вторжении ее оценивали в 190 тысяч вместе с «народными милициями ДНР и ЛНР», ...
- ^ Bengali, Shashank (18 February 2022). "The U.S. says Russia's troop buildup could be as high as 190,000 in and near Ukraine". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 18 February 2022. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ Hackett, James, ed. (February 2021). The Military Balance 2021 (1st ed.). Abingdon, Oxfordshire: International Institute for Strategic Studies. p. 68. ISBN 978-1-03-201227-8. OCLC 1292198893. OL 32226712M.
- ^ a b The Military Balance 2022. International Institute for Strategic Studies. February 2022. ISBN 9781000620030 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 30, 2023". Institute for the Study of War. Retrieved 31 May 2023.
- ^ "Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, June 14, 2024". Institute for the Study of War. Retrieved 17 August 2023.
- ^ a b The Military Balance 2022. International Institute for Strategic Studies. February 2022. ISBN 9781000620030 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Ukraine", The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency, 2023-01-18, retrieved 2023-01-19
- ^ "Swimming rivers and faking illness to escape Ukraine's draft". BBC News. 17 November 2023. Retrieved 17 November 2023.
- ^ Plokhy, Serhii (16 May 2023). The Russo-Ukrainian War: From the bestselling author of Chernobyl. Penguin Books. ISBN 978-1-80206-179-6.
... If the collapse of the USSR was sudden and largely bloodless, growing strains between its two largest successors would develop into limited fighting in the Donbas in 2014 and then into all-out warfare in 2022, causing death, destruction, and a refugee crisis on a scale not seen in Europe since the Second World War.
- ^ Ramani 2023, p. 74.
- ^ D'Anieri 2023, p. i; 98.
- ^ Roth, Andrew (17 December 2021). "Russia issues list of demands it says must be met to lower tensions in Europe". the Guardian. Retrieved 5 January 2025.
- ^ Marples, David R. (3 July 2022). "Russia's war goals in Ukraine". Revue Canadienne des Slavistes. 64 (2–3): 207–219. doi:10.1080/00085006.2022.2107837. ISSN 0008-5006.
- ^ Hinton, Alex (25 February 2022). "Putin's claims that Ukraine is committing genocide are baseless, but not unprecedented". The Conversation. Retrieved 15 December 2024.
- ^ Al Jazeera Staff. "'No other option': Excerpts of Putin's speech declaring war". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 15 December 2024.
- ^ "Nationalist and Imperial Thinking Define Putin's Vision for Russia". rusi.org. Retrieved 15 December 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Etkindwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ McGlynn, Jade (23 April 2024). "Russia Is Committing Cultural Genocide in Ukraine". Foreign Policy. Retrieved 4 July 2024.
- ^ Stavljanin, Dragan (2 April 2024). "Genocide Scholar: 'I Do Think that Russia's Violence in Ukraine is Genocidal'". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. Retrieved 4 July 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
v008was invoked but never defined (see the help page).