
Back أكسيد السكانديوم Arabic اسکاندیوم اوکسید AZB Oxid skanditý Czech Scandiumoxid German اسکاندیوم اکسید Persian Skandiumoksidi Finnish Oxyde de scandium French स्कैण्डियम(III) ऑक्साइड Hindi Ossido di scandio Italian 酸化スカンジウム(III) Japanese
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Scandium(III) oxide
| |
| Other names
Scandia, scandium sesquioxide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.844 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Sc2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 137.910 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Density | 3.86 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 2,485 °C (4,505 °F; 2,758 K) |
| insoluble in water | |
| Solubility | soluble in hot acids (reacts) |
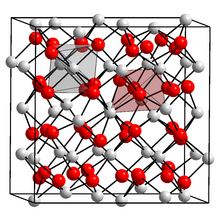
| Structure[1] | |
| Bixbyite | |
| Ia3 (No. 206) | |
a = 985 pm
| |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Scandium(III) sulfide |
Other cations
|
Yttrium(III) oxide Lutetium(III) oxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Scandium(III) oxide or scandia is a inorganic compound with formula Sc2O3. It is one of several oxides of rare earth elements with a high melting point. It is used in the preparation of other scandium compounds as well as in high-temperature systems (for its resistance to heat and thermal shock), electronic ceramics, and glass composition (as a helper material).
