
Back Càstig corporal escolar Catalan Lerneja korpa puno Esperanto Castigo corporal escolar en los Estados Unidos Spanish Châtiment corporel scolaire French Puniment corporal escolar Occitan Castigo físico escolar nos Estados Unidos Portuguese Телесные наказания в школах в США Russian
Corporal punishment, sometimes referred to as "physical punishment" or "physical discipline",[2] has been defined as the use of physical force, no matter how light, to cause deliberate bodily pain or discomfort in response to undesired behavior.[3] In schools in the United States, corporal punishment takes the form of a school teacher or administrator striking a student's buttocks with a wooden paddle (often called "spanking" or "paddling").[2]
The practice was held constitutional in the 1977 Supreme Court case Ingraham v. Wright, where the Court held that the "cruel and unusual punishments" clause of the Eighth Amendment did not apply to disciplinary corporal punishment in public schools, being restricted to the treatment of prisoners convicted of a crime.[4] In the years since, a number of U.S. states have banned corporal punishment in public schools.[2] The most recent state to outlaw it was Idaho in 2023,[5] and the latest de facto statewide ban was in Kentucky on November 2, 2023, when the last school district in the state that had not yet banned it did so. In 2014, a student was struck in a U.S. public school an average of once every 30 seconds.[6]
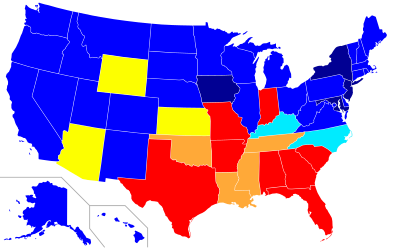
As of 2024, corporal punishment is still legal in private schools in every U.S. state except Illinois, Iowa, Maryland, New Jersey and New York, legal in public schools in 17 states, and practiced in 12 of the states.[citation needed].
Corporal punishment in school has been outlawed in Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Japan, South Korea, Israel, and just about every developed country in Europe, which makes the United States one of only two developed countries where corporal punishment in school is still allowed, the other being Singapore. The practice is banned in 128 countries.[7]
- ^ Anderson, Melissa (December 15, 2015). "Where Teachers Are Still Allowed to Spank Students". The Atlantic. Washington DC.
- ^ a b c Gershoff, E.T. (2008). Report on Physical Punishment in the United States: What Research Tells Us About Its Effects on Children (PDF). Columbus, OH: Center for Effective Discipline. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 27, 2016. Retrieved December 3, 2015.
- ^ Gershoff, E.T. (2017). "School corporal punishment in global perspective: prevalence, outcomes, and efforts at intervention". Psychology, Health & Medicine. 22 (1): 224–239. doi:10.1080/13548506.2016.1271955. PMC 5560991. PMID 28064515.
- ^ Oluwole, Joseph (September 23, 2014). "Ingraham v. Wright". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
lymanwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Strauss, Valerie (September 18, 2014). "19 states still allow corporal punishment in school". The Washington Post.
- ^ "School spankings are banned just about everywhere around the world except in US". The Conversation. London. July 31, 2019.