
Back مثبطات استرداد السيروتونين الانتقائية Arabic সিলেক্টিভ সেরোটোনিন রিআপটেক ইনহিবিটর Bengali/Bangla Inhibidor selectiu de la recaptació de serotonina Catalan Sōng-dĕk-sáng Háik-chĭng-só Cái-siék-chṳ̄ Ék-cié-câ CDO Selektivní inhibitor zpětného vychytávání serotoninu Czech Selektive serotoningenoptagshæmmere Danish Serotonin-Wiederaufnahmehemmer German Εκλεκτικός αναστολέας επαναπρόσληψης σεροτονίνης Greek Selektiva malhelpaĵo de realpreno de serotonino Esperanto Inhibidor selectivo de la recaptación de serotonina Spanish
| Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
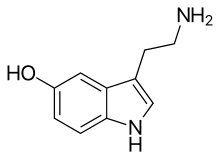 Serotonin, the neurotransmitter that is involved in the mechanism of action of SSRIs | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Synonyms | Serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitors, serotonergic antidepressants[1] |
| Use | Major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders |
| ATC code | N06AB |
| Biological target | Serotonin transporter |
| Clinical data | |
| Drugs.com | Drug Classes |
| Consumer Reports | Best Buy Drugs |
| External links | |
| MeSH | D017367 |
| Legal status | |
| In Wikidata | |
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs increase the extracellular level of the neurotransmitter serotonin by limiting its reabsorption (reuptake) into the presynaptic cell.[2] They have varying degrees of selectivity for the other monoamine transporters, with pure SSRIs having strong affinity for the serotonin transporter and only weak affinity for the norepinephrine and dopamine transporters.
SSRIs are the most widely prescribed antidepressants in many countries.[3] The efficacy of SSRIs in mild or moderate cases of depression has been disputed[4] and may or may not be outweighed by side effects, especially in adolescent populations.[5][6][7][8]
- ^ Barlow DH, durand VM (2009). "Chapter 7: Mood Disorders and Suicide". Abnormal Psychology: An Integrative Approach (Fifth ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning. p. 239. ISBN 978-0-495-09556-9. OCLC 192055408.
- ^ "Mechanism of Action of Antidepressants" (PDF). Psychopharmacology Bulletin. 36. Summer 2002. S2CID 4937890. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-02-28.
- ^ Preskorn SH, Ross R, Stanga CY (2004). "Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors". In Preskorn SH, Feighner HP, Stanga CY, Ross R (eds.). Antidepressants: Past, Present and Future. Berlin: Springer. pp. 241–262. ISBN 978-3-540-43054-4.
- ^ Rettew D (2022-07-26). "Depression and Serotonin: What the New Review Actually Says". Psychology Today. Retrieved 2024-09-26.
- ^ Kramer P (7 Sep 2011). "In Defense of Antidepressants". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 12 July 2011. Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- ^ Fournier JC, DeRubeis RJ, Hollon SD, Dimidjian S, Amsterdam JD, Shelton RC, Fawcett J (January 2010). "Antidepressant drug effects and depression severity: a patient-level meta-analysis". JAMA. 303 (1): 47–53. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1943. PMC 3712503. PMID 20051569.
- ^ Pies R (April 2010). "Antidepressants work, sort of – our system of care does not". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 30 (2): 101–104. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e3181d52dea. PMID 20520282. Archived from the original on 2017-09-13. Retrieved 2019-11-08.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:0was invoked but never defined (see the help page).