
Back زيغ كروي Arabic Сферична аберация Bulgarian Aberració esfèrica Catalan Sférická aberace Czech Sfærisk aberration Danish Abbildungsfehler#Sphärische Aberration German Σφάλμα σφαιρικής εκτροπής Greek Aberración esférica Spanish Aberrazio esferiko Basque ابیراهی کروی Persian
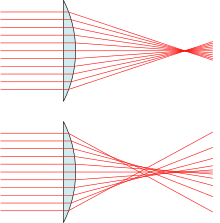
The bottom example depicts a real lens with spherical surfaces, which produces spherical aberration: The different rays do not meet after the lens in one focal point. The further the rays are from the optical axis, the closer to the lens they intersect the optical axis (positive spherical aberration).
(Drawing is exaggerated.)

In optics, spherical aberration (SA) is a type of aberration found in optical systems that have elements with spherical surfaces. This phenomenon commonly affects lenses and curved mirrors, as these components are often shaped in a spherical manner for ease of manufacturing. Light rays that strike a spherical surface off-centre are refracted or reflected more or less than those that strike close to the centre. This deviation reduces the quality of images produced by optical systems. The effect of spherical aberration was first identified in the 11th century by Ibn al-Haytham who discussed it in his work Kitāb al-Manāẓir.[1]
- ^ Boudrioua, Azzedine; Rashed, Roshdi; Lakshminarayanan, Vasudevan (2017-08-15). Light-Based Science: Technology and Sustainable Development, The Legacy of Ibn al-Haytham. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-351-65112-7.