
Back Stoigiometrie Afrikaans تكافؤ ترابط العناصر Arabic Estequiometría AST Стэхіяметрыя Byelorussian Стехиометрия Bulgarian Stehiometrija BS Estequiometria Catalan Stechiometrie Czech Støkiometri Danish Stöchiometrie German
Stoichiometry (/ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɪtri/ ⓘ) is the relationships between the masses of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions.
Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products, leading to the insight that the relations between quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of the products can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.
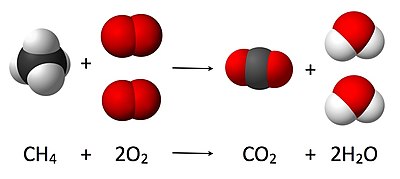
This is illustrated in the image here, where the balanced equation is:
- CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O
Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. This particular chemical equation is an example of complete combustion. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products and reactants that are produced or needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the quantities of methane and oxygen that react to form carbon dioxide and water.
Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.
Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, because of the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead in calculating the mass ratio.