
Back سكسنيل كولين Arabic سوکسینیل کولین AZB Succinilcolina Catalan Suxamethonium German Succinilcolina Spanish سوکسینیل کولین Persian Suksametoni Finnish Suxaméthonium French סוקסיניל כולין HE Սուկցինիլխոլին Armenian
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌsʌksɪnɪlˈkoʊliːn/ |
| Trade names | Quelicin, Anectine, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, intramuscular |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | NA |
| Metabolism | By pseudocholinesterase, to succinylmonocholine and choline |
| Onset of action | 30–60 sec (IV), 2–3 min (IM) |
| Duration of action | < 10 min (IV), 10–30 min (IM) |
| Excretion | Kidney (10%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
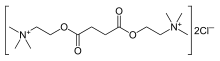
| Formula | C14H30Cl2N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 361.30 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Suxamethonium chloride (brand names Scoline and Sucostrin, among others), also known as suxamethonium or succinylcholine, or simply sux in medical abbreviation,[5] is a medication used to cause short-term paralysis as part of general anesthesia.[6] This is done to help with tracheal intubation or electroconvulsive therapy.[6] It is administered by injection, either into a vein or into a muscle.[7] When used in a vein, onset of action is generally within one minute and effects last for up to 10 minutes.[7]
Common side effects include low blood pressure, increased saliva production, muscle pain, and rash.[7] Serious side effects include malignant hyperthermia, hyperkalemia and allergic reactions.[8][9] It is not recommended in people who are at risk of high blood potassium or a history of myopathy.[6] Use during pregnancy appears to be safe for the baby.[10]
Suxamethonium is in the neuromuscular blocker family of medications and is of the depolarizing type.[7] It works by blocking the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscles.[7]
Suxamethonium was described as early as 1906 and came into medical use in 1951.[5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[11] Suxamethonium is available as a generic medication.[7]
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ "Product monograph brand safety updates". Health Canada. February 2024. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ "Anectine- succinylcholine chloride injection, solution". DailyMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine. 17 September 2018. Retrieved 23 November 2020.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Quelicin FDA labelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Lee C, Katz RL (March 2009). "Clinical implications of new neuromuscular concepts and agents: so long, neostigmine! So long, sux!". Journal of Critical Care. 24 (1): 43–49. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2008.08.009. PMID 19272538.
- ^ a b c World Health Organization (2009). Stuart MC, Kouimtzi M, Hill SR (eds.). WHO Model Formulary 2008. World Health Organization. pp. 426–8. hdl:10665/44053. ISBN 9789241547659.
- ^ a b c d e f "Succinylcholine Chloride". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ "Anectine Injection - Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) - (eMC)". www.medicines.org.uk. 12 January 2016. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 16 December 2016.
- ^ "Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: December 22, 2020". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (Press release). 22 December 2020. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Prescribing medicines in pregnancy database". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 16 December 2016. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 16 December 2016.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.