
Back سائل زلالي Arabic Líquid sinovial Catalan شلەی جومگەیی CKB Synovia German Sinovia likvo Esperanto Líquido sinovial Spanish Liigesevõie Estonian Likido sinobial Basque مایع زلالهای Persian Liquide synovial French
| Synovial fluid | |
|---|---|
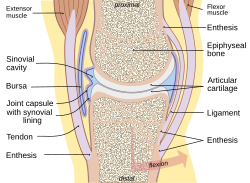 A typical joint | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | synovia |
| MeSH | D013582 |
| TA98 | A03.0.00.031 |
| TA2 | 1535 |
| FMA | 12277 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Synovial fluid, also called synovia,[help 1] is a viscous, non-Newtonian fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints. With its egg white–like consistency,[1] the principal role of synovial fluid is to reduce friction between the articular cartilage of synovial joints during movement.[2] Synovial fluid is a small component of the transcellular fluid component of extracellular fluid.
- ^ West, Sterling G. (2015). Rheumatology secrets. The secrets series (3rd ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier Mosby. p. 19. ISBN 9780323037006. OCLC 908716294.
- ^ Petty, Ross E. (2016-01-01), Petty, Ross E.; Laxer, Ronald M.; Lindsley, Carol B.; Wedderburn, Lucy R. (eds.), "Chapter 2 - Structure and Function", Textbook of Pediatric Rheumatology (Seventh Edition), Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 5–13.e2, doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-24145-8.00002-8, ISBN 978-0-323-24145-8, retrieved 2020-10-18