
Back Tetrasiklien Afrikaans تيتراسايكلن Arabic تتراسایکیلین AZB Тетрациклин Bulgarian টেট্রাসাইক্লিন Bengali/Bangla Tetraciklin BS Tetraciclina Catalan تێتڕاسایکلین CKB Tetracyklin Czech Tetracyclin Welsh
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌtɛtrəˈsaɪkliːn/ |
| Trade names | Tetracyn |
| Other names | TE/TET/TC/TCY[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682098 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80% |
| Metabolism | Not metabolized |
| Elimination half-life | 8–11 hours, 57–108 hours (kidney impairment) |
| Excretion | Urine (>60%), feces |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.438 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
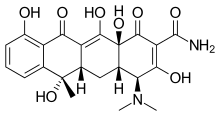
| Formula | C22H24N2O8 |
| Molar mass | 444.440 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections,[3] including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis.[3] It is available in oral and topical formulations.[4][5]
Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and loss of appetite.[3] Other side effects include poor tooth development if used by children less than eight years of age, kidney problems, and sunburning easily.[3] Use during pregnancy may harm the baby.[3] It works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria.[3]
Tetracycline was patented in 1953[6] and was approved for prescription use in 1954.[7][8] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[9] Tetracycline is available as a generic medication.[3] Tetracycline was originally made from bacteria of the genus Streptomyces.[3]
- ^ "Antibiotic abbreviations list". Retrieved 22 June 2023.
- ^ "Tetracycline". PubChem. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Tetracycline". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 28 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ "Tetracycline Topical Dosage Guide + Max Dose, Adjustments". Drugs.com. Retrieved 27 November 2024.
- ^ "Tetracycline Dosage Guide + Max Dose, Adjustments". Drugs.com. Retrieved 27 November 2024.
- ^ U.S. patent 2699054A
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Historywas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 489. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.